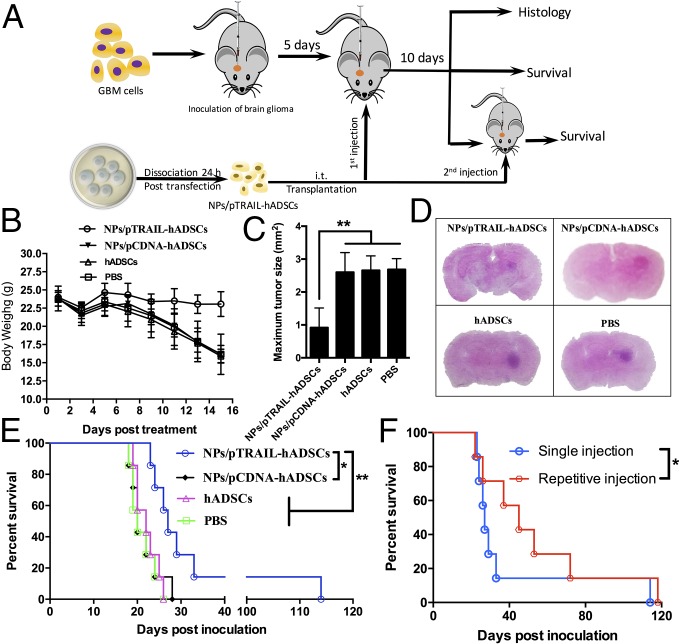
Fig. 5.
TRAIL-overexpressing hADSCs inhibited GBM growth and extended survival in a mouse GBM model in vivo. (A) Schematic of experimental design. NPs/pTRAIL-engineered hADSCs, hADSCs (3 × 105 cells), or PBS solution were administered i.t. to glioma-bearing mice at day 5 after glioma (7 × 105 cells) inoculation. For the repetitive injection group, the second dose of NPs/pTRAIL-engineered hADSCs was given at day 10 after the first dose. (B) Changes in body weight of mice as a function of time in intracranial glioma-bearing mice (n = 7). (C) Tumor size was determined by histologic analysis at day 15 after tumor inoculation (n = 3 per treatment group; **P < 0.01). (D) Representative photographs of H&E staining from each group show tumor growth. (Magnification, 1×.) (E) Survival curve of intracranial glioma-bearing mice after treatment with a single dose of NPs/pTRAIL-engineered hADSCs, hADSCs (3 × 105 cells), or PBS solution. (F) Survival after treatment with repetitive doses of NPs/pTRAIL-engineered hADSCs. For E and F, survival analysis was conducted by a log-rank test based on the Kaplan–Meier method (n = 7 per treatment group; *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01).