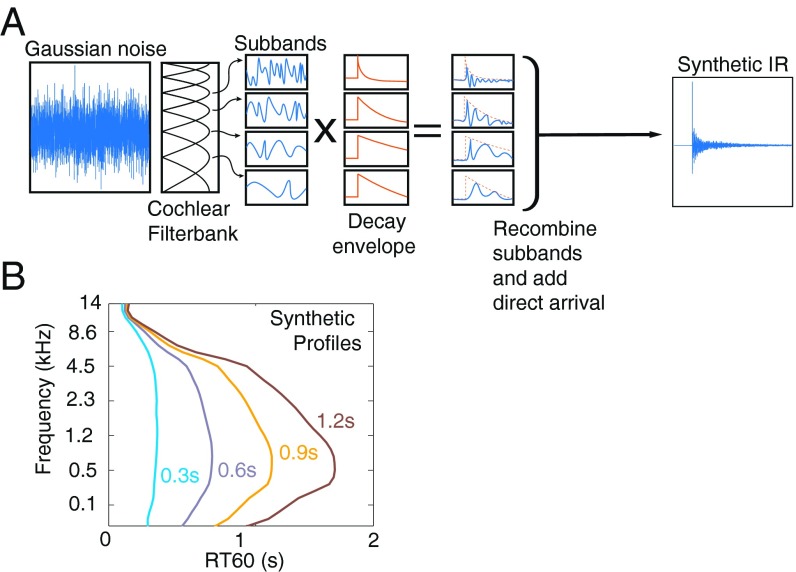
Fig. 5.
Synthetic IR generation. (A) IRs were generated by filtering Gaussian noise into cochlear subbands and multiplying each subband by an amplitude envelope. The modified subbands were then recombined to yield a broadband synthetic IR. The temporal form of the decaying envelopes and the frequency dependence of decay rates were manipulated to produce IRs that either were consistent with the statistics of real-world IRs or deviated from them in some respect. (B) Synthetic decay rate profiles were computed that shared the variation in frequency and the variation of decay-rate profile with average RT60 with the surveyed IR distribution (Fig. 4C).