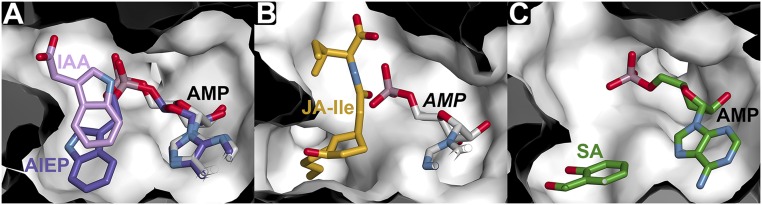
Fig. S1.
Comparison of GH3 protein acyl acid binding sites. Surface views of the acyl acid binding sites of AtGH3.5 (A), AtGH3.11 (B), and AtGH3.12 (C) highlight the structural difference in each enzyme. Each view is oriented to show the binding of acyl acids relative to the nucleotide site. (A) AtGH3.5 active site. The positions of IAA (pink) and AMP (white) were determined crystallographically (Figs. 2 and 3) with the position of AIEP (purple) from the VvGH3.1 structure (13) overlaid on the AtGH3.5•AMP•IAA complex structure. (B) AtGH3.11 active site. Binding of JA-Ile in the crystal structure reveals a larger active site to accommodate the oxylipin moiety of JA (9). The location of AMP is modeled based on the AtGH3.5 structure and is shown only for reference. (C) The AtGH3.12 active site. The crystallographically determined positions of SA, an inhibitor of AtGH3.12, and AMP (both ligands in green) are shown (9).