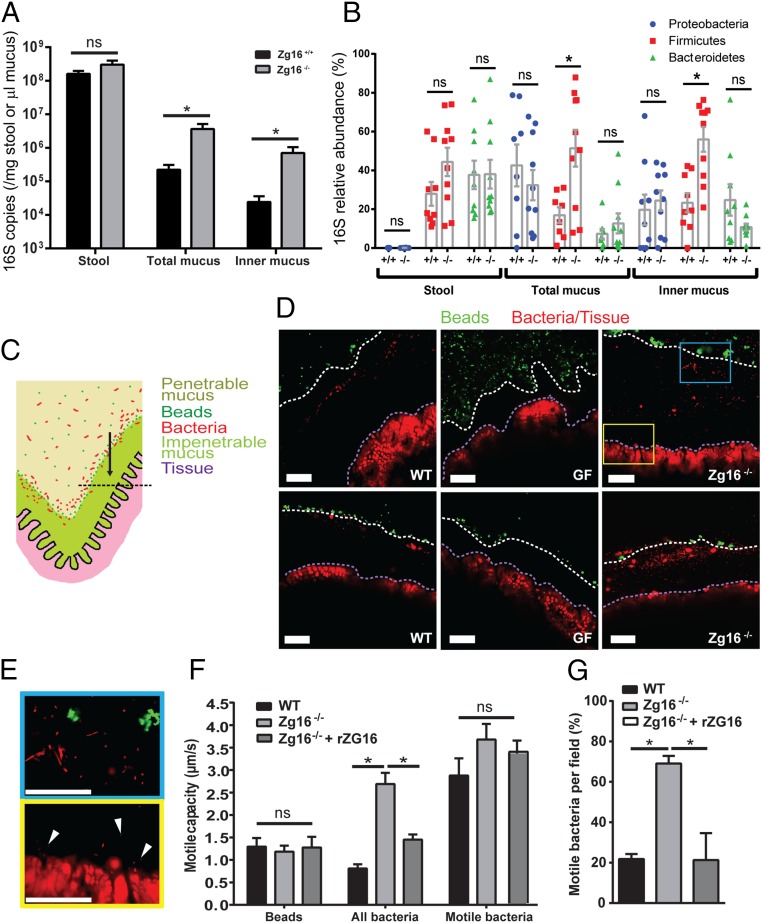
Fig. 3.
ZG16 alters the mucus-associated intestinal microbiota as well as the distribution and motile capacity of bacteria within the mucus. (A) Zg16+/+ and Zg16−/− littermate bacterial 16S copy number detected in stool and unflushed (total mucus) or flushed (inner mucus) colonic tissue samples by qPCR. Data were normalized to stool mass or mucus volume (SI Appendix, Fig. S6). (B) Group-specific qPCR showing an increased abundance of Gram-positive Firmicutes in the total and inner mucus of the Zg16−/− in relation to littermate Zg16+/+ mice. (C–E) Conventionally raised C57BL/6 (WT), germ-free (GF), and Zg16−/− distal colon tissues were mounted in an imaging chamber; fluorescent beads were applied apically to visualize the interface between the impenetrable (IM) and penetrable (PM) mucus layers; and bacteria and tissues were visualized in situ using the nucleic acid-binding dye, Syto9. Mucus, bacteria, and tissues were imaged. (C) Schematic representation of chamber-mounted colonic tissues with IM and PM layers, beads, and bacteria indicated. Black dashed line represents the focal plane where confocal optical sections were acquired. (D) Confocal micrographs through WT, GF, and Zg16−/− colonic mucus. White dashed lines indicate the IM/PM interface; purple dashed lines indicate the edge of the colonic tissue. (E) Magnified confocal micrographs from the Inset blue and yellow boxes in D. (Top, blue border) Morphologically distinctive bacteria in the mucus. (Bottom, yellow border) Bacteria (white arrows) near the tissue surface. (F and G) Bacterial motility in WT, Zg16−/−, and Zg16−/− + rZG16 mucus was assessed by recording 1-min time series of optical sections through the colonic mucus as pictured in E (Movies S1–S7). (F) Quantification of motile capacity (maximum velocity) of beads at the IM/PM interface, all bacteria within the mucus, and only bacteria classed as motile within the mucus. (G) Proportion of bacteria determined as motile per imaging field. All error bars are SEM from n = 9 Zg16+/+ and n = 10 Zg16−/−animals. Statistical significances calculated with Mann–Whitney u test (A, B) or Sidak’s (F) or Dunn’s (G) multiple comparison tests (ns, not significant; *P < 0.05). (All scale bars, 50 µm.)