Fig. 2.
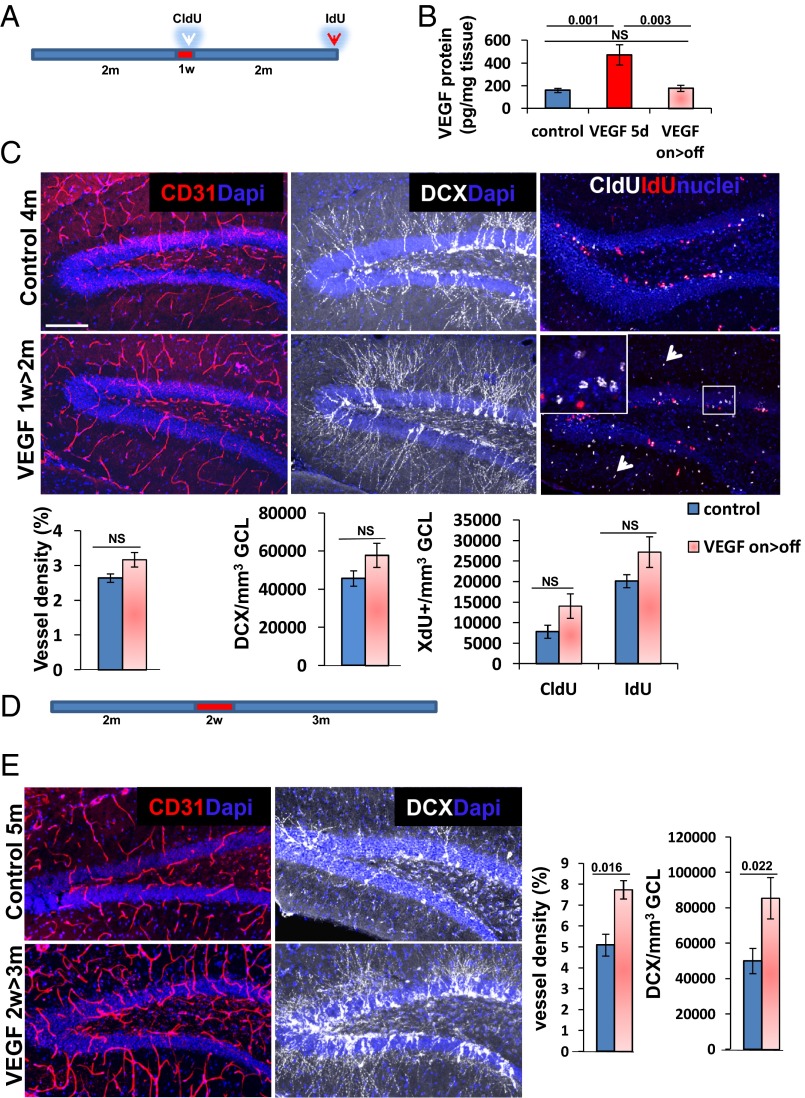
VEGF fails to increase neurogenesis in the absence of newly induced durable vessels. (A) VEGF was induced in 2-mo-old mice for 1 wk and then deinduced, and the hippocampus was examined 2 mo thereafter. CldU was injected by the end of the on period, and IdU was injected just before euthanasia. (B) ELISA of hippocampal VEGF in animals killed 5 d postinduction (VEGF 5d) and in animals induced for 2 wk and deinduced for an additional 2 wk (on>off). (C) Immunostaining and quantification for CD31, DCX, and incorporated thymidine analogs. Note no significant differences in MVD and neurogenesis between the controls and on>off group despite a previous exposure to VEGF. Also note the incorporation of CldU in cells in the molecular layer of on>off animals (arrowheads) as an indication of efficient VEGF induction. (D) VEGF was induced for 2 wk and deinduced for 3 mo. (E) CD31 and DCX immunohistochemistry showing that induced vessels and neurogenesis both persist long term after 2 wk of VEGF exposure. NS, not significant. (Scale bar: C and E, 100 μm.)