Figure 3.
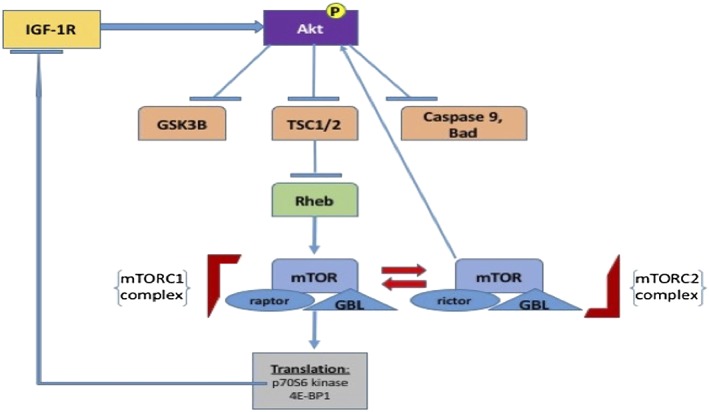
A selection of downstream targets of AKT is displayed. Following upstream activation, in this case by insulin‐like growth factor receptor 1 (IGF‐1R) signalling, AKT phosphorylates and inactivates three key downstream effectors: glycogen synthase kinase‐3 beta (GSK3B), tuberous sclerosis 1 and 2 (TSC1/2) and the proapotosis proteins caspase 9 and Bad. Inhibition of TSC1/2 leads to subsequent inhibition of Ras homologue enriched in brain (Rheb) and the downstream conversion of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTORC) 2 to mTORC1. This ultimately leads to the phosphorylation of p70S6 kinase and 4E‐BP1, which favours an increase in ribosomal protein translation and cell growth. Phosphorylated p70S6 kinase normally exerts negative feedback by inhibiting IGF‐1R signalling; loss of this negative feedback loop occurs in cancer cells following treatment with mTOR inhibitors. GBL, G protein beta protein subunit‐like
