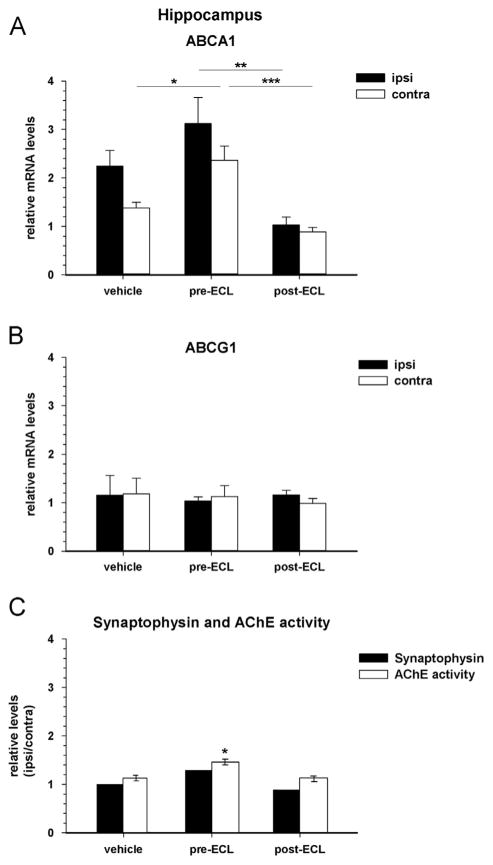
Fig. 6.
Quantification of ABCA1 and ABCG1 gene expressions in the hippocampus of entorhinal cortex-lesioned mice following LXR agonist treatments: Prevention versus Rescue. Target mRNA expression levels relative to actin were determined by real time-PCR in the ipsilateral (ipsi) and contralateral (contra) hippocampus (HPC) of entorhinal cortex-lesioned (ECL) mice, treated with an LXR agonist prior to (pre-ECL) or after (post-ECL) the lesion. Bars indicate the mean of 5 mice/group±SEM at 25 days post-lesion (DPL). (A) ABCA1 expression is significantly increased in the contra-lateral (*p = 0.02) HPC of the LXR pre-lesion treatment group (prevention) compared to the corresponding vehicle group when assessed during the active synaptic remodeling process at 25 DPL. In contrast, administration of the LXR agonist after the lesion (rescue) decreased ABCA1 expression (ipsi: *p = 0.004; contra: ***p = 0.001) compared to the corresponding pre-ECL administration group during the remodeling process. (B) ABCG1 expression is not modified in the HPC of any group at 25 DPL. (C) Synaptophysin protein levels ratios in the HPC of LXR pre-ECL and post-ECL treated mice at 25 DPL. Synaptophysin protein levels were assessed by Western blot in duplicate analysis of pools of 5 hippocampi in the ipsi- and contra-lateral HPC and the ratio ipsilateral:contralateral was calculated for both pre- and post-ECL groups. This assessment served as an indicator of synaptic plasticity in order to determine whether the LXR treatment effects on ABC transporters expression coincide with reinnervation following the ECL as measured by AChE staining. An increase in synaptophysin protein levels ratio is observed in the pre-ECL but not post-ECL treated mice compared to vehicle treated mice while AChE staining in the outer molecular layer of the dentate gyrus was found to be significantly increased also in the pre-ECL (prevention) as opposed to the post-ECL (rescue) agonist treatment group (*p<0.02).