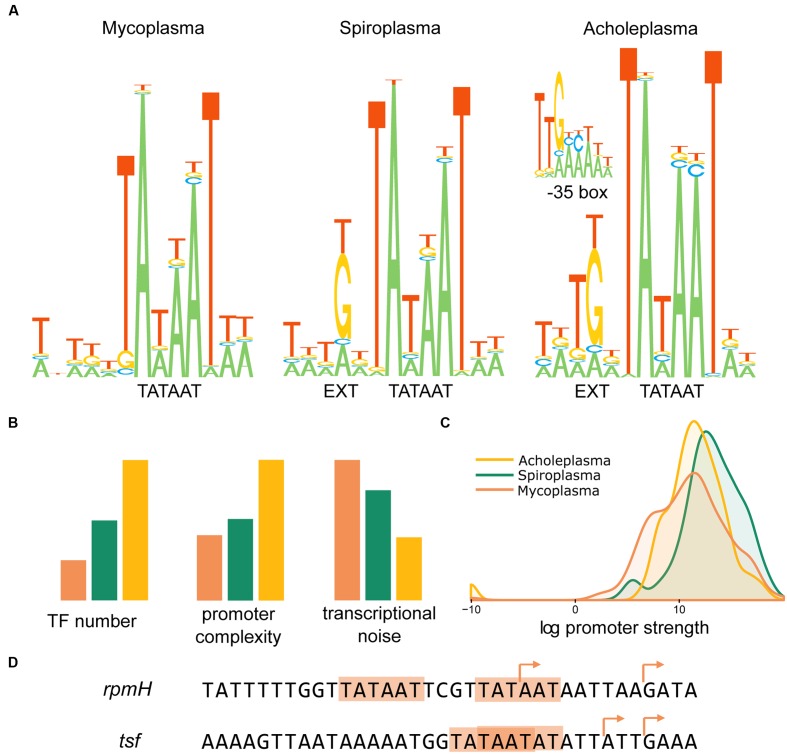
FIGURE 3.
Promoter structure of Acholeplasma laidlawii, Spiroplasma melliferum, and Mycoplasma gallisepticum. (A) Core-promoter structure in three species. (B) The complexity of transcriptional control in three species. Promoter complexity was measured as the number of nucleotides with high informational content. Transcriptional noise was measured as the relative number of intragenic and antisense promoters. (C) The dynamic range of the promoters’ strength in three species. The strength of the promoter was measured as the normalized number of reads covering TSS. (D) Examples of tandem promoters in M. gallisepticum. Arrows indicate experimentally validated TSSs.