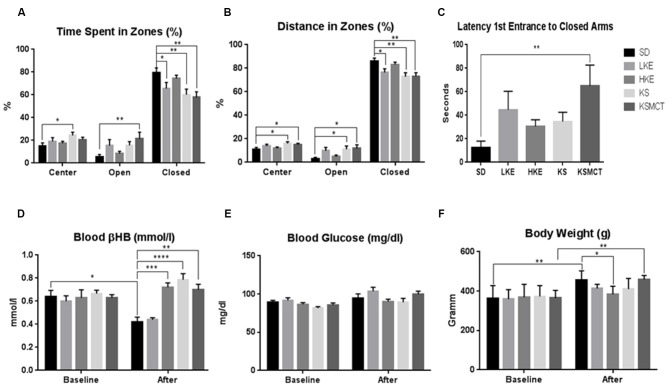
Figure 1.
Response of Sprague-Dawley (SPD) rats to chronic feeding of exogenous ketone supplementation. (A) Rats consuming KSMCT supplements spent more time in open arms (open), Low-dose ketone ester (LKE), KS and KSMCT groups spent less time in closed arms (closed), showing reduced anxiety compared to control (SD) group; (B) Rats consuming ketone supplements traveled more distance in open arms (KS and KSMCT) and less in closed arms (LKE, KS and KSMCT), showing reduced anxiety compared to control group; (C) Rats consuming KSMCT entered the closed arms later, showing reduced anxiety compared to control group; (D) Rats consuming high dose ketone ester (HKE), KS and KSMCT showed elevated blood ketone levels after 13 weeks (after) compared to control group; (E) Blood glucose levels did not change significantly were lower in HKE and KSMCT groups compared to control after 13 weeks; and (F) body weight was lower in HKE group after 13 weeks compared to control. Abbreviations: SD, standard rodent chow + water (~25 g/kg b.w. water/day); LKE, SD + LKE (1,3-butanediol-acetoacetate diester, ~10 g/kg b.w./day); HKE, SD + HKE (~25 g/kg b.w./day); KS, SD + beta-hydroxybutyrate-mineral salt (βHB-S; ~25 g/kg b.w./day); KSMCT, SD + βHB-S+medium chain triglyceride (MCT; ~25 g/kg b.w./day); (*p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001).