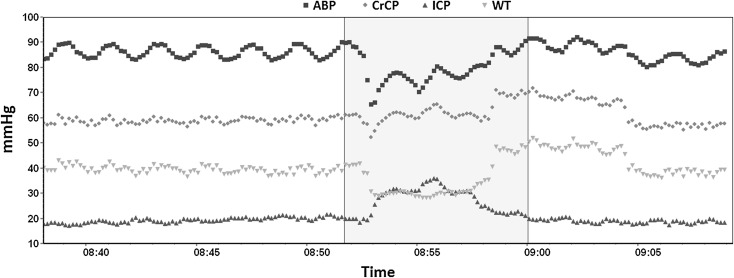
Fig. 4.
Representation of the CrCP interaction with ICP and WT in a situation of intracranial hypertension observed in a traumatic brain-injured patient (source: Brain Physics Laboratory TBI Database, University of Cambridge). During the increase of ICP, the CrCP also increases and WT decreases as an effect of preserved autoregulation. ABP arterial blood pressure, CrCP critical closing pressure, ICP intracranial pressure, WT wall tension, TBI traumatic brain injury