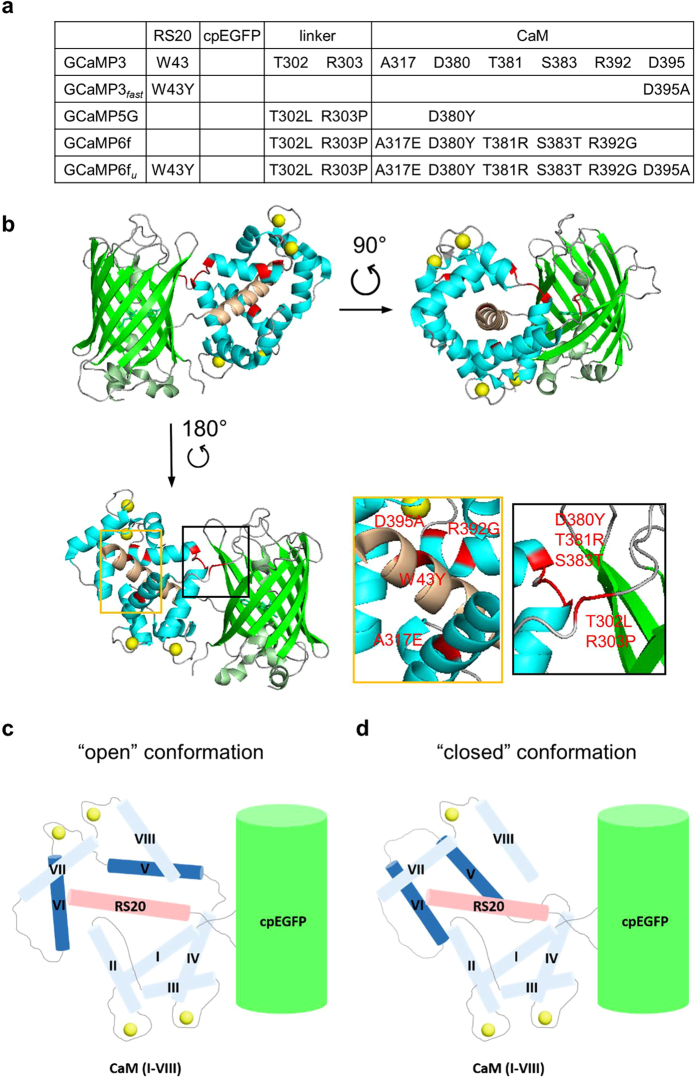
Figure 5. Comparison of fast GCaMP probes (GCaMP3fast and GCaMP6fu) and their parent variants (GCaMP3 and GCaMP6f).
(a) Position of the mutations that gave rise to GCaMP3fast and GCaMP6fu variants, relative to GCaMP3. (b) Crystal structure of monomeric GCaMP6m in a Ca2+-bound form with cpEGFP (green), Ca2+ ions (yellow), CaM (blue) and the RS20 peptide (light brown) (adapted from Ding et al.,27 PDB 3WLD). The amino acid residues highlighted in red are those that generated GCaMP6fu relative to GCaMP3. Schematic representation of (c) Ca2+-bound GCaMP3/GCaMP6f showing “open” conformation of EF-hand 3 (helices V and VI); (d) Ca2+-bound GCaMP3fast/GCaMP6fu showing “closed” conformation of disabled EF-hand 3 (helices V and VI).