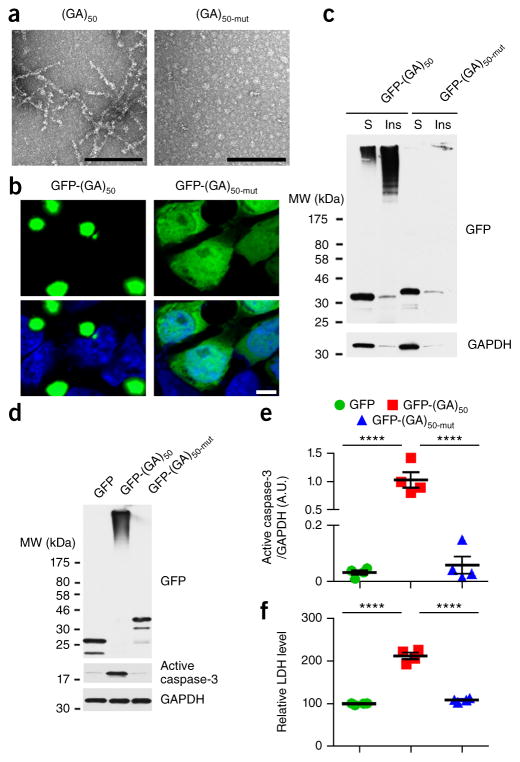
Figure 1.
Disrupting the conformation of poly(GA) proteins inhibits poly(GA) protein aggregation and toxicity. (a) Transmission electron micrographs of purified recombinant untagged (GA)50 and (GA)50-mut proteins. Scale bars, 200 nm. (b) Confocal micrographs of GFP-(GA)50 and GFP-(GA)50-mut proteins expressed in HEK293T cells. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst 33258 (blue). Scale bar, 5 μm. (c) Immunoblot analysis of Triton X-100–soluble (S) and –insoluble (Ins) fractions of lysates from HEK293T cells expressing GFP-(GA)50 and GFP-(GA)50-mut. Blots were probed with antibodies specific for GFP. (d,e) Immunoblot (d) and densitometric analysis of immunoblots (e) indicating the levels of GFP-tagged proteins and active caspase-3 in neurons expressing GFP, GFP-(GA)50 or GFP-(GA)50-mut. GAPDH was used as a loading control in c and d. Full-length immunoblots are presented in Supplementary Figure 9. (f) Relative LDH activity, an indicator of cell toxicity, in the culture supernatant of primary neuronal cells expressing the indicated GFP-tagged proteins. Data are presented as mean ± s.e.m. from four separate experiments. P < 0.0001, as analyzed by one-way ANOVA. ****P < 0.0001, Tukey’s post hoc analysis. A.U., Arbitrary units