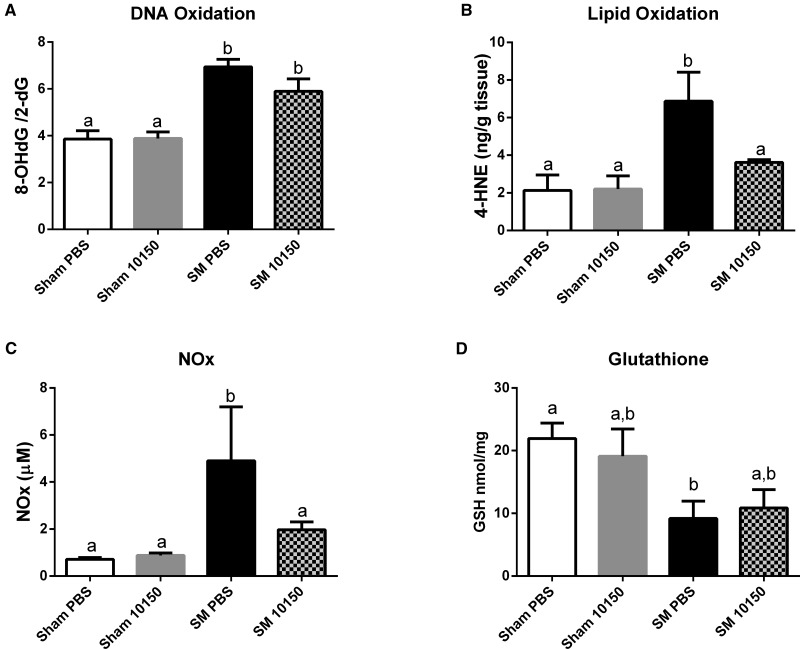
FIG. 3.
Effect of catalytic antioxidant treatment on SM-mediated increase in oxidative/nitrosative stress biomarkers. Animals exposed to 1.4 mg/kg SM or EtOH vehicle (Sham) and treated with either q4 hours AEOL 10150 or q4 hours PBS. Groups of animals were euthanized 24 h post-SM exposure. Pulverized left lung tissue samples were analyzed using HPLC for DNA oxidation (A). Lipid peroxidation was analyzed in lung tissue homogenate by measuring 4-HNE by GC/MS (B). BALF samples were analyzed for Total NO2/NO3 levels using a plate reader assay (C). Reduced glutathione concentrations were measured in lung tissue by HPLC. Data is presented as mean ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA with Newman–Keuls post-test corrected for multiple comparisons was performed to determine differences between groups, bars with different letters are significantly different from one another (P < .05). (A–D) Sham PBS n = 17, Sham 10150 n = 19, SM PBS n = 8, SM 10150 n = 7.