Fig. 4.
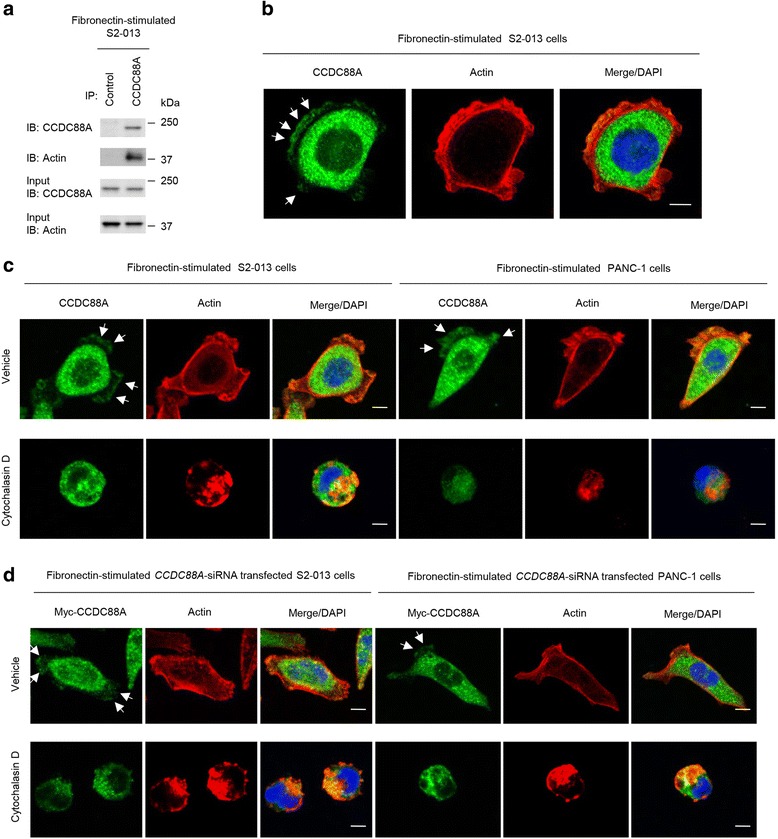
Co-localization of CCDC88A with actin-filaments in cell protrusions. a. Immunoprecipitation (IP) of CCDC88A from S2-013 cells cultured on fibronectin. Proteins within the immunoprecipitates were examined by western blotting. The blots were probed with antibodies against CCDC88A and actin. Mouse IgG isotype control antibody was used as an isotype control. b. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images show nuclear DAPI staining (blue), abundant cytoplasmic CCDC88A, and the accumulation of CCDC88A (green) in membrane protrusions of fibronectin-stimulated S2-013 cells. Actin filaments were labeled with phalloidin (red). Arrows, CCDC88A that was colocalized with actin-filaments in cell protrusions. Bar, 10 μm. c. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images of S2-013 and PANC-1 cells that were pretreated with 100 μM Cytochalasin D for 12 h and were then incubated on fibronectin. Cells were stained with anti-CCDC88A antibody (green). Actin filaments were labeled with phalloidin (red). Arrows, CCDC88A that was colocalized with actin-filaments in cell protrusions. Blue, DAPI staining. Bars, 10 μm. d. Confocal immunofluorescence microscopic images. CCDC88A-siRNA transfected S2-013 and PANC-1 cells, which were transiently transfected with a myc-tagged CCDC88A-rescue construct, were pretreated with 100 μM Cytochalasin D for 12 h, and were subsequently incubated on fibronectin. Cells were stained with anti-myc antibody (green). Actin filaments were labeled with phalloidin (red). Arrows, CCDC88A that was colocalized with actin-filaments in cell protrusions. Blue, DAPI staining. Bars, 10 μm
