Figure 2.
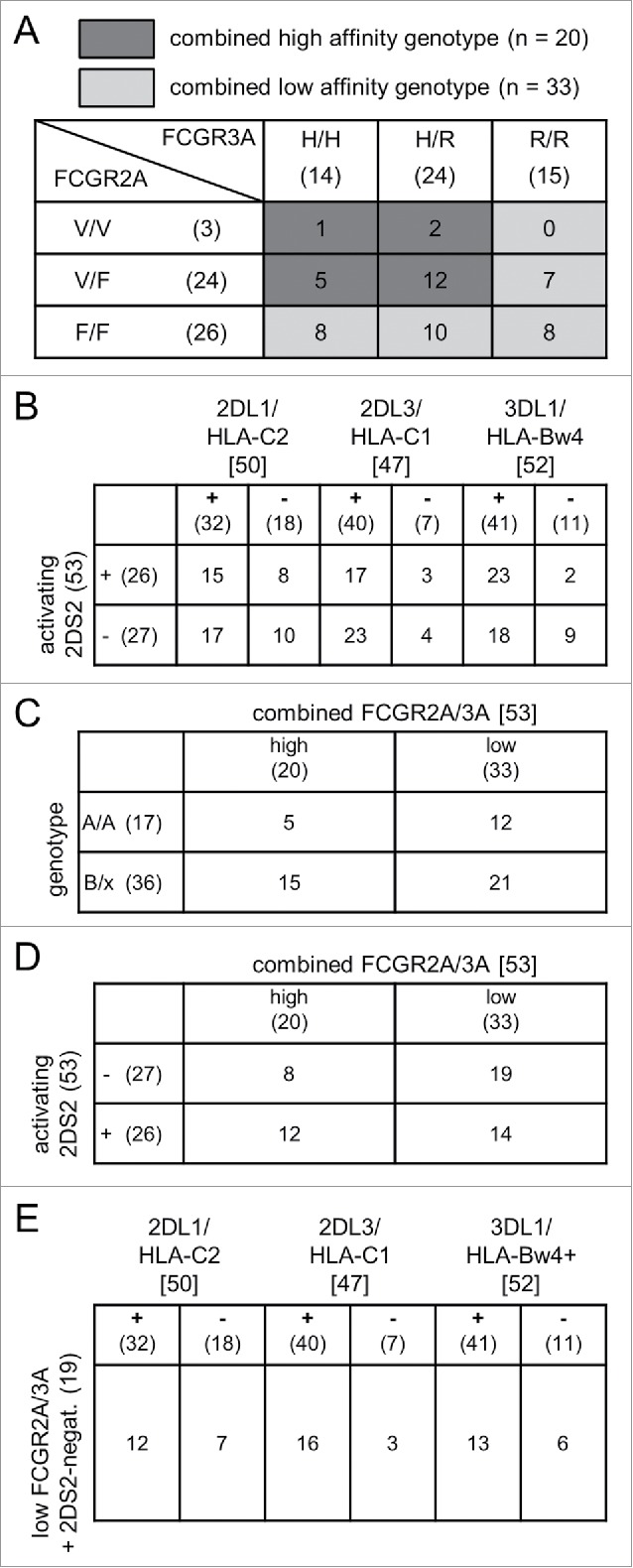
(A) Frequencies of FCGR2A/3A and KIR/KIRL genotypes. The total number of patients with distinct FCGR2A (lines) and 3A polymorphisms (columns) are shown in parentheses. Numbers without parentheses indicate patients with combinations of FCGR2A and 3A polymorphisms. Groups of patients with combined high- and low-affinity genotypes were defined as follows: combined high affinity (dark gray; FCGR2A H/H or H/R and FCGR3A V/V or V/F) and combined low affinity (light gray; FCGR2A R/R and/or F/F). (B) Frequencies of genotypes with inhibitory KIR/KIRL match and mismatch with or without the activating KIR 2DS2. The columns indicate the total number of patients with inhibitory KIR (2DL1, 2DL3, 3DL1) in square brackets. Numbers in round brackets reflect patient numbers with match (+) and mismatch (−) with the respective KIRL (HLA-C2, HLA-C1, HLA-Bw4). The lines show the number of patients in round brackets with presence (+) or absence (−) of activating KIR 2DS2. Numbers of patients without brackets indicate distinct combinations of inhibitory KIR/KIRL match- and activating KIR 2DS2 status. (C) Combination of FCGR2A/3A high and low genotype with genotype B/x and A/A. The columns indicate the total number of patients with combined high- and low-affinity FCGR2A/3A in round brackets. The lines show the number of patients with genotype A/A or B/x in round brackets. Numbers of patients without brackets indicate distinct combinations of combined high- and low-affinity FCGR2A/3A and genotype A/A or B/x. (D) Combination of FCGR2A/3A high and low genotype with or without the activating KIR 2DS2. The columns indicate the total number of patients with combined high- and low-affinity FCGR2A/3A in round brackets. The lines show the number of patients in round brackets with presence (+) or absence (−) of the activating KIR 2DS2. Numbers of patients without brackets indicate distinct combinations of combined high- and low-affinity FCGR2A/3A and 2DS2 status. (E) Frequencies of combined 2DS2-negative and FCGR2A/3A low-affinity genotype with or without KIR/KIRL match. Nineteen patients with combined low-affinity FCGR2A/3A phenotype and absent activating KIR 2DS2 were analyzed for inhibitory KIR/KIRL match and mismatch. The columns indicate the total number of patients with inhibitory KIR (2DL1, 2DL3, 3DL1) in square brackets. Numbers in round brackets reflect patient numbers with match (+) and mismatch (−) with the respective KIRL (HLA-C2, HLA-C1, HLA-Bw4). Numbers of patients without brackets indicate distinct combinations of inhibitory KIR/KIRL match- and absent activating KIR 2DS2 status.
