Figure 5.
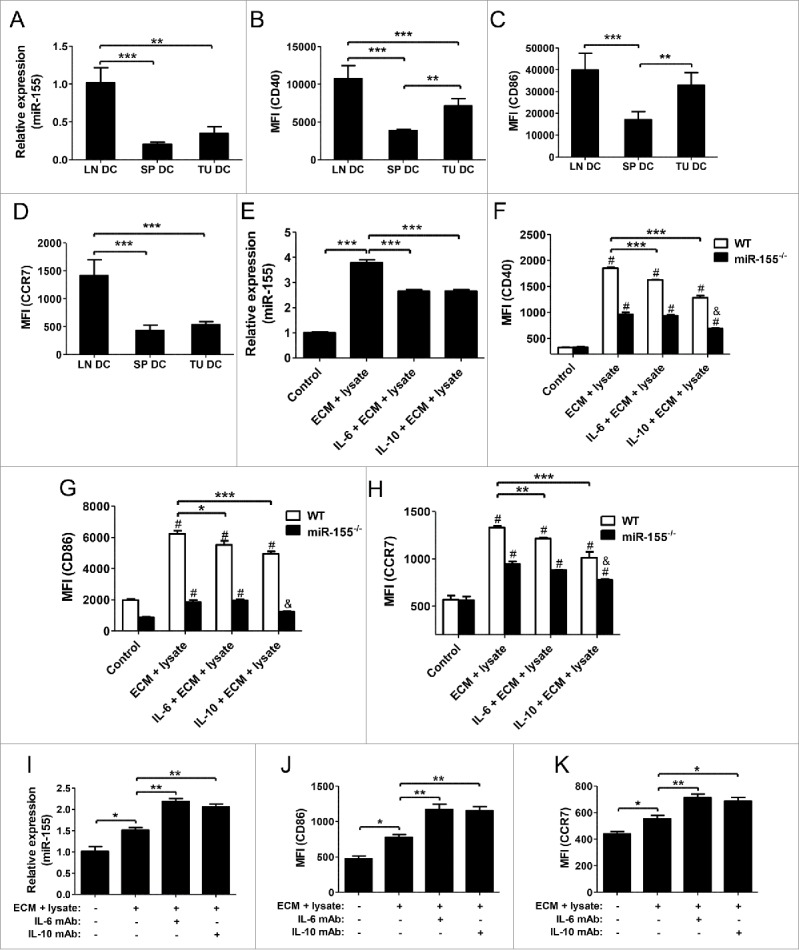
IL-6 and IL-10 inhibit DC maturation through suppressing miR-155. (A) miR-155 expression in lymph node DCs, splenic DCs, and tumor-infiltrating DCs of tumor-bearing WT mice was detected by RT-PCR (n = 3). (B)–(D) CD40 (B), CD86 (C), and CCR7 (D) expression levels on above DCs were determined by flow cytometry under the same voltage and compensation conditions (n = 3). (E)–(H) WT BMDCs were pretreated with IL-6 (100 ng/mL) or IL-10 (50 ng/mL) for 24 h prior to the additional treatment with EO771 tumor cell lysate and ECM; cells without ECM plus cell lysate treatment were used as negative control (n = 3). Expression levels of miR-155 (E) and CD40 (F), CD86 (G), and CCR7 (H) were determined by RT-PCR and flow cytometry, respectively. (I)–(K) To neutralize IL-6 and IL-10 in ECM, IL-6 mAb (5 μg/mL), or IL-10 mAb (1 μg/mL) was added into the treatment medium and incubated for 2 h at 37°C before BMDC stimulation (n = 3). Expression of miR-155 (I), CD86 (J), and CCR7 (K) were determined by RT-PCR and flow cytometry, respectively. (A)–(E) and (I)–(K) one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparison test; (F)–(H) two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey multiple comparison test. #p < 0.05 versus their respective control group; &p < 0.05 relative to positive control; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
