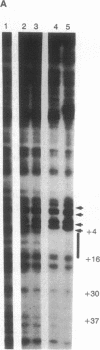
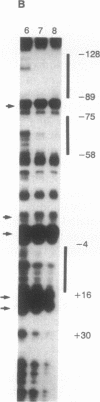
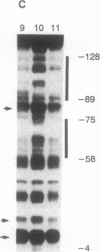
Abstract
Regulation of human thyrotropin beta subunit gene (TSHB) expression by thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) was examined in a clonal rat pituitary-cell line (GH3). Transient expression studies were done with various 5'-flanking DNA sequences of TSHB coupled to reporter gene chloramphenicol acetyltransferase. Deletion analysis defined two discrete regions (-128 to -92 base pairs and -28 to +8 base pairs) that each mediated an approximately 2-fold TRH induction. The upstream site contains a DNA sequence with close homology to the DNA-binding site for a pituitary-specific transcriptional factor Pit-1/GHF-1. DNase I footprinting analysis of mouse thyrotropic tumor extract as well as DNA-transfection studies using an expression vector containing an N-terminal deletion of Pit-1/GHF-1 cDNA suggest that Pit-1/GHF-1 or a closely related protein in the thyrotroph mediates TRH responsiveness of this gene. In addition, the downstream site overlaps with the recently characterized thyroid hormone-inhibitory element of TSHB. In fact, deletion of DNA sequences important in thyroid hormone-receptor binding (c-erbAB/c-ERBA2) from +3 to +8 base pairs, significantly reduced (30%) TRH responsiveness. The location of a TRH-stimulatory element near a thyroid hormone-inhibitory element may allow for fine control of TSHB expression in vivo.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa T., Koizumi Y., Yamada T., Tawata M., Nagata H., Izumiyama T., Yoshizawa K. Difference in pituitary-thyroid feedback regulation in hypothyroid patients, depending on the severity of hypothyroidism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978 Sep;47(3):560–565. doi: 10.1210/jcem-47-3-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Karin M. A pituitary-specific trans-acting factor can stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter in extracts of nonexpressing cells. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent G. A., Harney J. W., Chen Y., Warne R. L., Moore D. D., Larsen P. R. Mutations of the rat growth hormone promoter which increase and decrease response to thyroid hormone define a consensus thyroid hormone response element. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Dec;3(12):1996–2004. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-12-1996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnside J., Darling D. S., Carr F. E., Chin W. W. Thyroid hormone regulation of the rat glycoprotein hormone alpha-subunit gene promoter activity. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6886–6891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr F. E., Burnside J., Chin W. W. Thyroid hormones regulate rat thyrotropin beta gene promoter activity expressed in GH3 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Apr;3(4):709–716. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-4-709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr F. E., Shupnik M. A., Burnside J., Chin W. W. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates the activity of the rat thyrotropin beta-subunit gene promoter transfected into pituitary cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Apr;3(4):717–724. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-4-717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee V. K., Lee J. K., Rentoumis A., Jameson J. L. Negative regulation of the thyroid-stimulating hormone alpha gene by thyroid hormone: receptor interaction adjacent to the TATA box. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9114–9118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Kalla K., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Cell-specific expression of the prolactin gene in transgenic mice is controlled by synergistic interactions between promoter and enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):959–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darling D. S., Burnside J., Chin W. W. Binding of thyroid hormone receptors to the rat thyrotropin-beta gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Sep;3(9):1359–1368. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-9-1359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. N., Maurer R. A. The distal enhancer region of the rat prolactin gene contains elements conferring response to multiple hormones. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Jan;3(1):3–9. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-1-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Tashjian A. H., Jr Receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone in prolactin producing rat pituitary cells in culture. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6180–6186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Flynn S. E., Voss J. W., Albert V. R., Kapiloff M. S., Wilson L., Rosenfeld M. G. The POU-specific domain of Pit-1 is essential for sequence-specific, high affinity DNA binding and DNA-dependent Pit-1-Pit-1 interactions. Cell. 1990 Jun 15;61(6):1021–1033. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90067-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaji H., Hinkle P. M. Regulation of thyroid hormone receptors and responses by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH4C1 cells. Endocrinology. 1987 Nov;121(5):1697–1704. doi: 10.1210/endo-121-5-1697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Albert V. R., Elsholtz H. P., Lu L. I., Rosenfeld M. G. Activation of cell-specific expression of rat growth hormone and prolactin genes by a common transcription factor. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1400–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2831625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrone M. H., Hinkle P. M. Regulation of pituitary receptors for thyrotropin-releasing hormone by thyroid hormones. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jul 25;253(14):5168–5173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Chin W. W., Habener J. F., Ridgway E. C. Transcriptional regulation of the thyrotropin subunit genes by thyroid hormone. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2900–2903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shupnik M. A., Rosenzweig B. A., Showers M. O. Interactions of thyrotropin-releasing hormone, phorbol ester, and forskolin-sensitive regions of the rat thyrotropin-beta gene. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):829–836. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tashjian A. H., Jr Clonal strains of hormone-producing pituitary cells. Methods Enzymol. 1979;58:527–535. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(79)58167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wondisford F. E., Farr E. A., Radovick S., Steinfelder H. J., Moates J. M., McClaskey J. H., Weintraub B. D. Thyroid hormone inhibition of human thyrotropin beta-subunit gene expression is mediated by a cis-acting element located in the first exon. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14601–14604. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wondisford F. E., Usala S. J., DeCherney G. S., Castren M., Radovick S., Gyves P. W., Trempe J. P., Kerfoot B. P., Nikodem V. M., Carter B. J. Cloning of the human thyrotropin beta-subunit gene and transient expression of biologically active human thyrotropin after gene transfection. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-1-32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. M., Kao M. Y., Gordon D. F., Ridgway E. C. Thyroid hormone regulates the mouse thyrotropin beta-subunit gene promoter in transfected primary thyrotropes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14840–14847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]