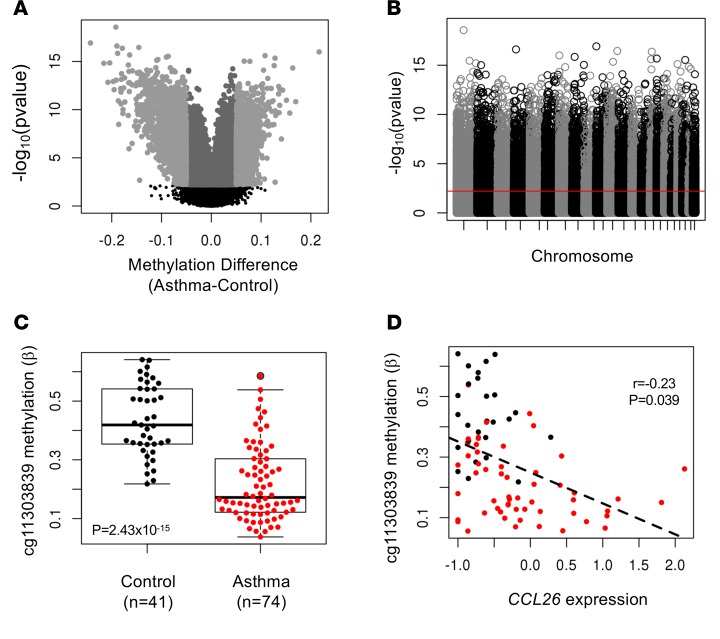
Figure 1. Differential methylation in airway epithelial cells from asthmatic and control subjects.
(A) Volcano plot showing methylation differences between asthmatic (n = 74) and nonasthmatic (n = 41) individuals. Mean differences in β values are shown on the x axis. Dark gray indicates CpGs that differ between asthmatics and nonasthmatics at q ≤ 0.05; light gray indicates CpGs with a fold change of >5%; The black dots indicate non-significant sites at a q > 0.05. (B) Manhattan plot of 327,271 CpGs in our analysis of asthma-associated differentially methylated CpG sites. P values (y axis) correspond to the differences in methylation between asthmatic and control subjects. The red line corresponds to the q value threshold (FDR 5%). (C) Box plot showing methylation levels at a CpG site (cg11303839) upstream of the transcription start site of CCL26 (encoding eotaxin 3), a chemokine elevated in the airways of asthmatic subjects. Box plot displays the median, first and third quartiles, and 95% confidence intervals. (D) Scatter plot showing the correlation between CCL26 transcript abundance and cg11303839 methylation levels for 81 individuals with both gene expression and methylation data. In C and D, black points are nonasthmatics and red are asthmatics.