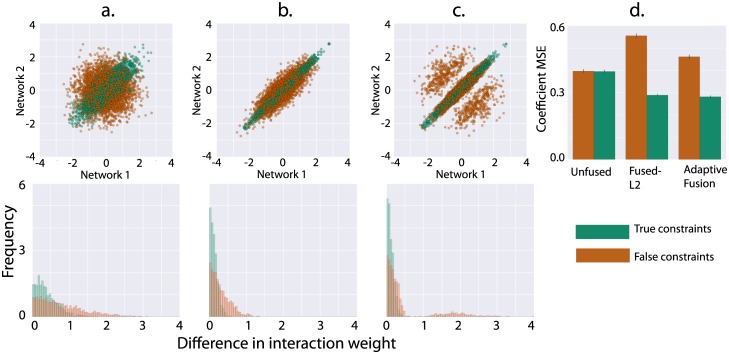
Fig 3. In order to evaluate the performance of adaptive fusion in the presence of non-conserved interactions, we performed a series of simulations inferring networks given a partially corrupted list of orthology mappings (or, orthology mappings that do not represent functional similarity).
Networks were generated with 35 TFs by 200 genes, 60% orthology coverage, 40% false orthology coverage, and 30 samples per network. A. Top: we plot the interaction weights between pairs of fused interactions in network 1 (x-axis) and network 2 (y-axis) following network inference without fusion (λS = 0). True fusion constraints are generated from pairs of true orthologs, while false fusion constraints derive from a pair of orthologs at least one of which is false. When λS = 0—equivalent to fitting the networks independently—interactions linked by false constraints are uncorrelated with one another, while interactions linked by true constraints are correlated, reflecting their functional similarity. Below we plot the distribution of differences in weights joined by true and false constraints; true constraints have differences on average closer to zero. B. shows the weights of interactions when networks are fit using fused-L2. In this condition, interactions bound by both true and false fusion constraints are forced to be very similar across the two species. C. With adaptive fusion, many of the false fusion constraints are relaxed. These constraints are no longer forced to be similar, and some of the original structure is restored. D. Shows the effect of fused-L2 and adaptive fusion on the accuracy of network recovery, as measured by MSE between the known simulated network weights and the inferred network weights. When fusion is introduced, recovery of the correctly fused part of the network improves, but the bias induced by fused-L2 degrades performance on the incorrectly fused part of the network. With adaptive fusion, the gains on the conserved part of the network are preserved with significantly less loss of accuracy on the non-conserved part of the network. Error bars are 95% confidence intervals on the squared error of coefficients.