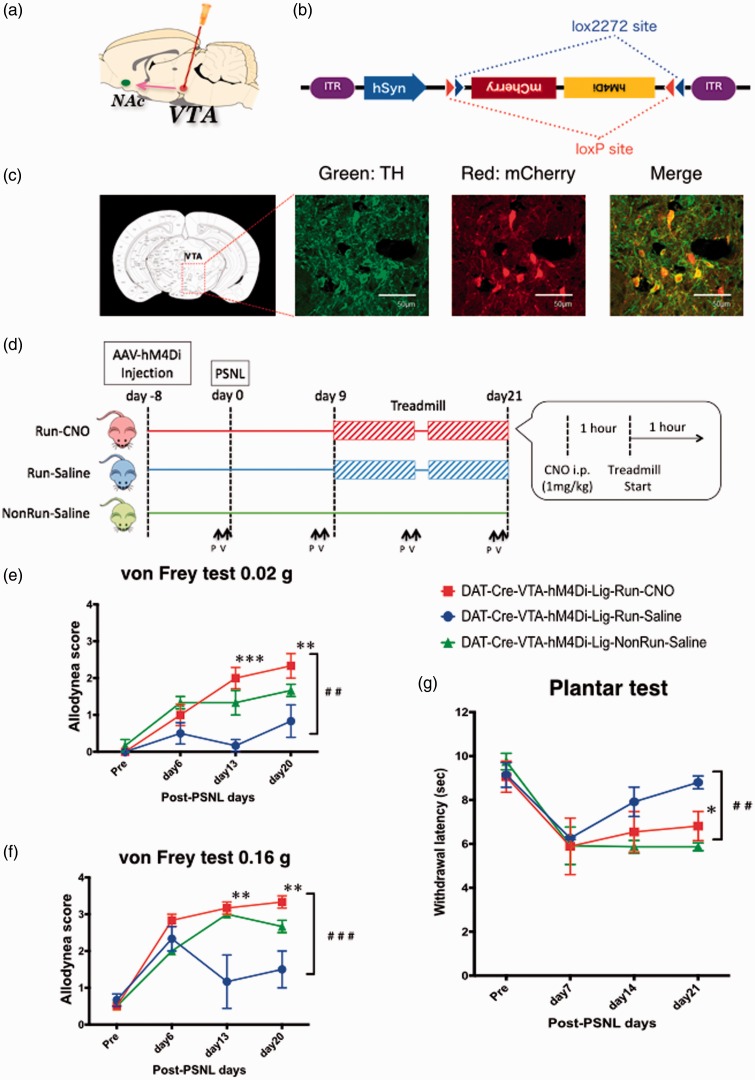
Figure 4.
Effect of specific pharmacogenetic suppression of VTA dopamine neural activity on EIH. (a) Injection site for AAV-hM4Di in VTA. (b) Schematic construct of AAV10-hM4Di. (c) Specific expression of the AVV-derived transgenes in the VTA of DAT-Cre/TG mice. Fluorescent immunostaining revealed mCherry-labeled hM4Di receptors (red) on TH-labeled dopamine neurons (green). Yellow in the merged picture represents colocalization of hM4Di and TH. (d) Schedule of the experimental protocol. AAV-hM4Di was injected at VTA in two weeks before the PSNL, subsequently the hM4Di expression induced by FLEX switch system was restricted to DAT positive cells. Treadmill exercise (6 m/min) was performed for two weeks from nine days after PSNL. CNO was injected an hour before the exercise everyday (1 mg/kg, i.p.). (e-g) Anti-EIH effect due to temporally suppressed activity of VTA dopamine neuron induced by Gi-DREADD system, measured by von Frey test (0.02 g (e) and 0.16 g (f)) and plantar test (g). Each point represents the mean ± SEM of three samples. ##p < 0.01, ###p < 0.001, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. VTA: ventral tegmental area; NAc: nucleus accumbens; PSNL: partial sciatic nerve ligation; P: planter test, V: Von Frey test.