Figure 2. Identification of an anti-HPA-1a avb3-specific subtype in +ICH cases after absorption of other subtypes with αIIbb3 beads.
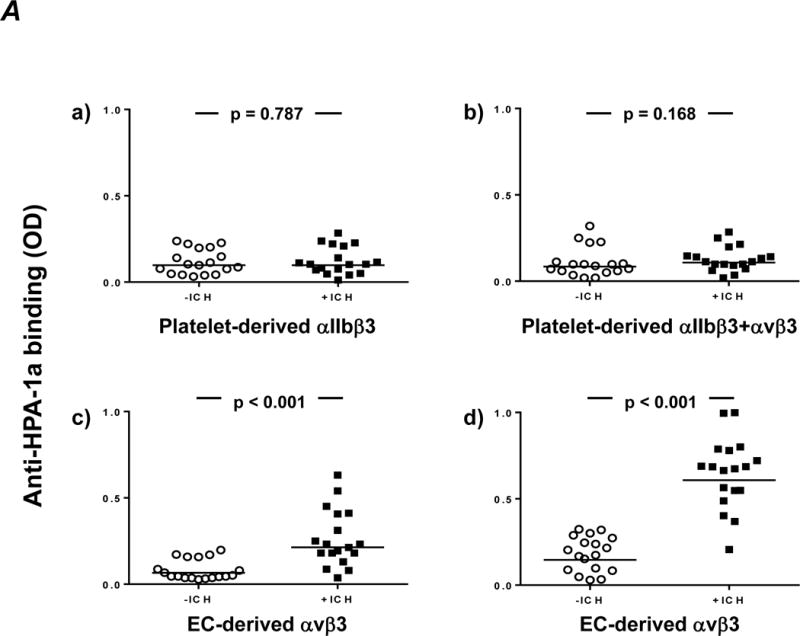
A. Maternal anti-HPA-1a antibodies (n=18 per cohort) were pre-absorbed with aIIbb3 beads to remove HPA-1a antibodies against aIIbb3 and b3. Afterwards, the absorbate was incubated with HPA-1aa platelets (upper panel) or endothelial cells (bottom panel) and moabs against aIIbb3 (a), avb3 (c) or b3 (b,d). After cell lysis, the trimolecular antigen-antibody complex was immobilized on microtiter wells coated with anti-mouse IgG. Binding of anti-HPA-1a antibodies was detected with horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-labeled anti-human IgG. Statistical analysis was performed by Mann-Whitney U Test. Note that after absorption, avb3-specific anti-HPA-1a remains detectable in the +ICH cohort only (c,d). This antibody specificity reacts more readily with avb3 immobilized with moab AP3 (d) than with avb3 immobilized with moab 23C6 (c), possibly indicating epitope interference.
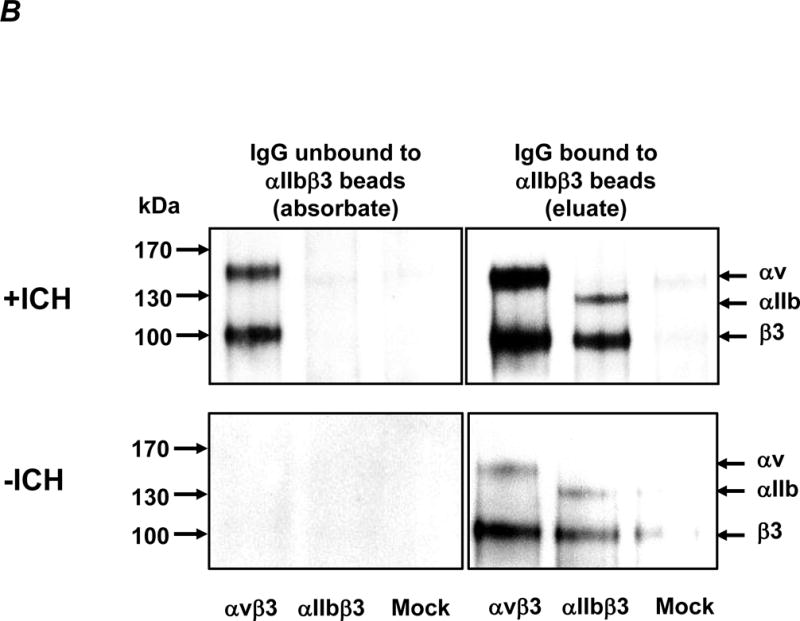
B. Maternal anti-HPA-1a antibodies from the +ICH (top) and −ICH (bottom) cohorts were absorbed with aIIbb3 beads. Unbound IgG (the absorbates) and bead-bound IgG (the eluates) were incubated with biotin-labelled transfected (avb3, aIIbb3) or non-transfected (mock) CHO cells, as indicated. After washings, CHO cells were lysed, the antigen-antibody complex was precipitated with protein-G coupled beads and separated on 10% SDS-PAGE under non-reducing conditions. After blotting, precipitated proteins were visualized by the use of enzyme-labeled streptavidin and a chemiluminescence system. In the –ICH cohort (bottom panel), all antibodies were removed by the beads as indicated by a non-reactive absorbate (left). Antibodies of anti-aIIbb3/anti-b3 specificity could be eluted from these beads (right). Note that anti-b3 is capable to pull down aIIbb3 and avb3 integrins. In contrast, in the +ICH cases (top panel), removal of anti-aIIbb3/anti-b3 antibodies leaves antibodies of anti-avb3 specificity behind (left). The eluate is reactive with both integrins, indicating presence of anti-b3/anti-aIIbb3 (right). One representative gel from n=9 independent experiments is shown.
