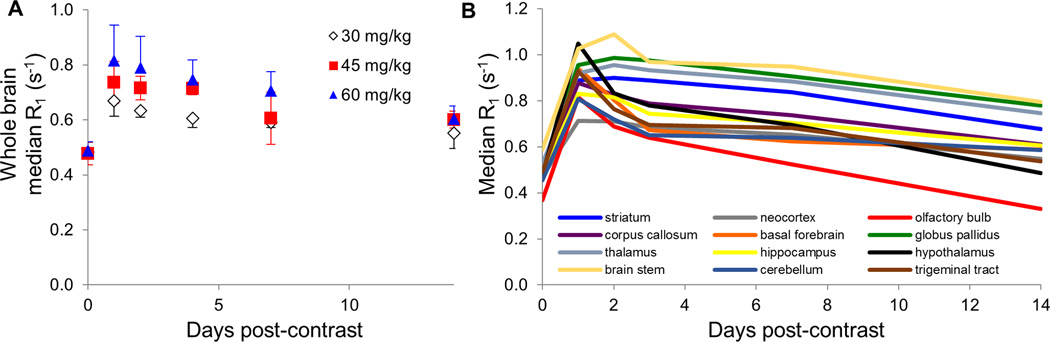
Figure 2.
Uptake of Mn in the whole brain and various brain regions measured with quantitative MRI. (A) Whole-brain average R1 relaxation rate reached a maximum 24 hours following contrast administration regardless of contrast dose ranging from 30–60 mg/kg MnCl2. Efflux from the brain was slow, with some enhancement remaining at the 14 day imaging time point. (B) Regional analysis of uptake of 60 mg/kg MnCl2 based on registration and segmentation of brain volumes to a rat brain atlas. Some brain regions (neocortex, corpus callosum, basal forebrain, hippocampus, hypothalamus, and cerebellum) reached maximum enhancement one day following contrast administration, while others (striatum, globus pallidus, thalamus, and brain stem) in some cases reached maximum at two or four days post-contrast.