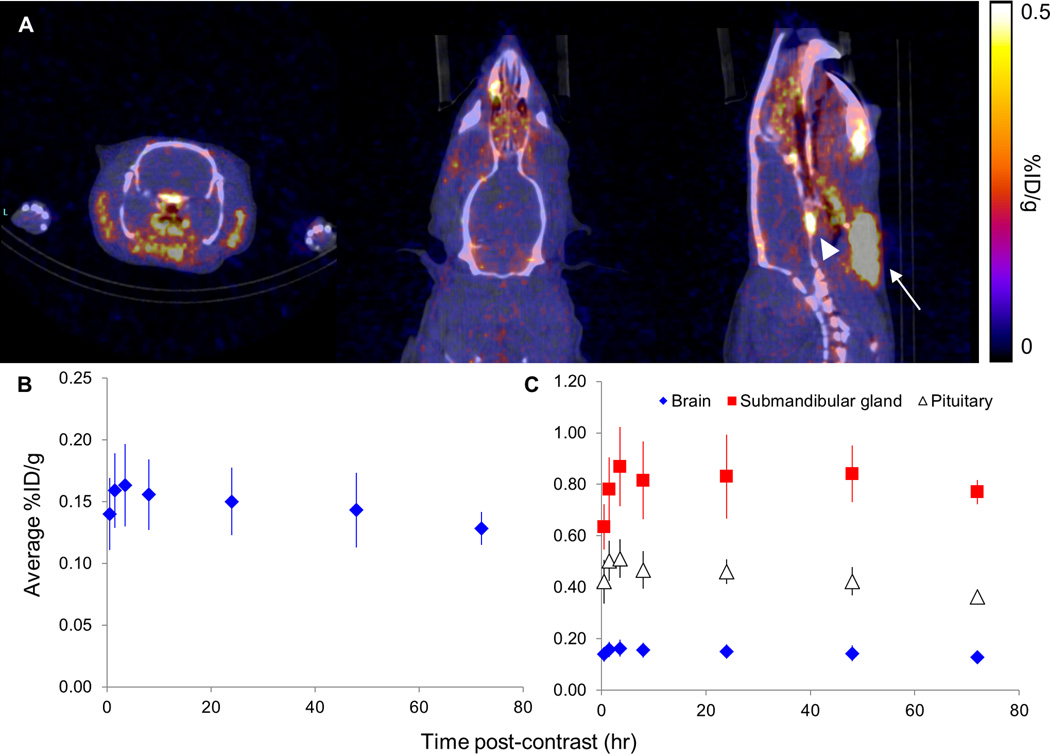
Figure 4.
In vivo PET/CT of brain uptake of NCA 52Mn in the rat. (A) Coronal, axial, and sagittal views of the brain (left to right, respectively) from in vivo PET/CT of a rat four hours following administration of no-carrier-added (NCA) 52Mn. Submandibular gland = white arrow, pituitary = white arrowhead. (B) In four subjects, average brain uptake reached a maximum at four hours following contrast administration, after which a slow decrease in brain signal was observed. (C) High 52Mn uptake in the submandibular gland and pituitary, up to 0.869 and 0.512 %ID/g respectively, were measured at all imaging time points.