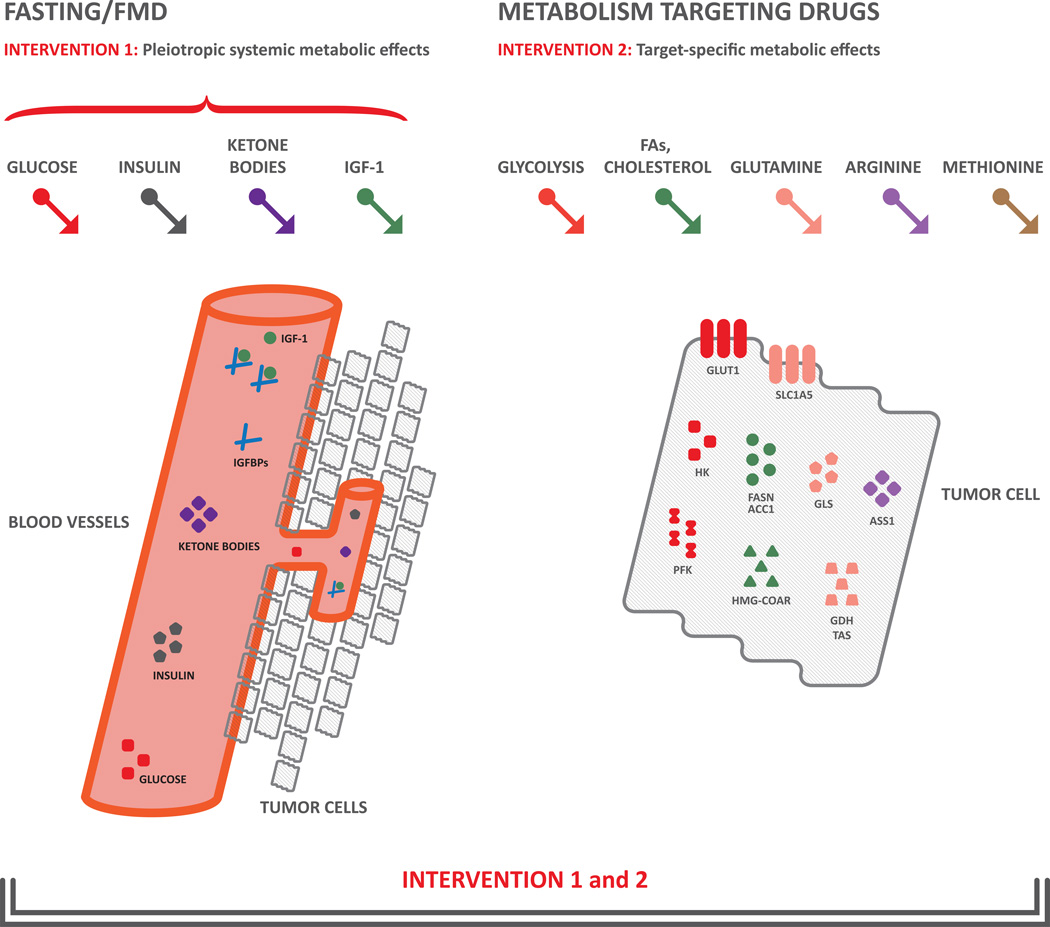
Figure 3. Rationale for combining dietary interventions and drugs targeting specific metabolic pathways in cancers.
Fasting and FMD (left part of the figure) impact on systemic metabolism through induction of pleiotropic metabolic effects, including reduction of glycemia, insulin and IGF-1 levels, and increase of ketone bodies and IGFBPs. On the other hand, pharmacologic approaches (right part of the figure) have the potential to selectively inhibit the specific metabolic pathway(s), such as glycolysis, glutamine, arginine, methionine, FAs and cholesterol metabolism, to which a single tumor may be addicted. Combining the two strategies could produce synergistic and selective anticancer effects .
Abbreviations. IGF-1: insulin-like growth factor 1; FAs: fatty acids; GLUT1: glucose transporter 1; HK: hexokinase; PFK: phosphofructokinase; FASN: fatty acid synthase; ACC1: acetyl-CoA carboxylase; HMGCR: hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase; GLS: glutaminase; GDH: glutamate dehydrogenase; TAs: transaminases; ASS1: argininosuccinate synthase 1