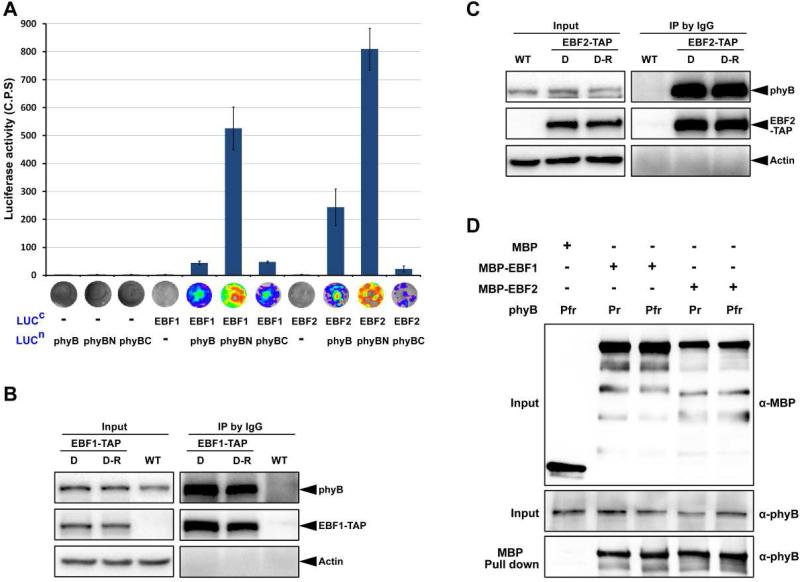
Figure 4. EBF1 and EBF2 directly associate with both the Pr and Pfr forms of phyB.
(A) LCI assay of the interactions of EBF1 and EBF2 with phyB in tobacco leaves. Full-length of EBF1 and EBF2 were fused to the split C-terminal (LUCc) fragments of luciferase. The full-length sequence, N-terminal and C-terminal fragments of phyB (phyB, phyBN, phyBC) were fused to the split luciferase N-terminus (LUCn). Empty vectors were used as negative controls. C.P.S is counts per second. Mean ± s.d., n=5.
(B and C) Co-immunoprecipitation assays for the interactions of EBF1 (B) or EBF2 (C) with phyB. Four-day-old dark-grown WT and transgenic seedlings over-expressing EBF1-TAP or EBF2-TAP seedlings were maintained in the dark (D) or exposed to red light (D-R) for 30 min. Proteins were extracted and immunoprecipitated using IgG Sepharose and immunoblotted using the indicated antibodies. Actin was used as a loading control.
(D) Pull-down assays to examine direct protein interactions in vitro. Recombinant phyB incubated with phycocyanobilin (Pfr) or methanol alone (Pr) was used as prey and pulled down using purified MBP, EBF1-MBP or EBF2-MBP proteins as bait.