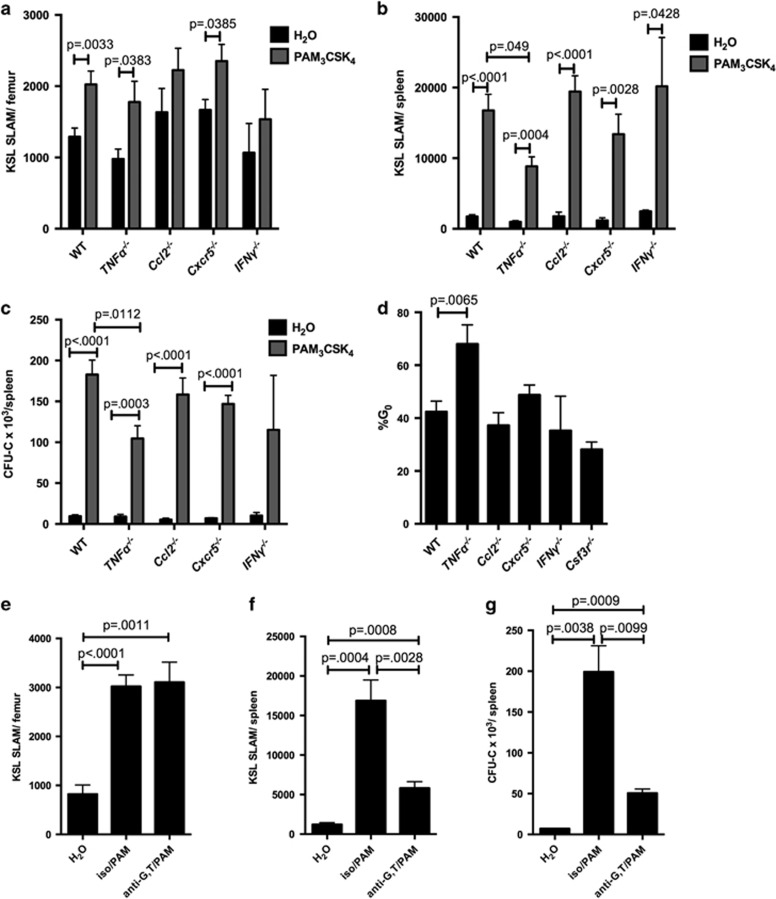
Figure 7.
TNFα contributes to PAM3CSK4-mediated spleen HSPC expansion. WT, TNFα−/−, Ccl2−/−, Cxcr5−/− and IFNγ−/− mice (6–8 weeks old) were treated with PAM3CSK4 (100 μg intraperitoneally (i.p.) q48 h × 3 doses, analyzed 24 h after final dose) or water alone. Shown are the KSL SLAM cells per femur (a) and spleen (b). (c) Whole spleen cells from PAM3CSK4-treated mice or water-treated controls were plated on complete methylcellulose, and colonies counted after 7 days of growth at 37 °C. (d) Following PAM3CSK4 treatment, the cell cycle status of KSL SLAM cells in the spleen of mice of the indicated genotypes were determined by flow cytometry using Ki-67 and DAPI. (n=4–12 mice per group). (e–g) WT mice were treated with PAM3CSK4 as described above, and in addition some mice received G-CSF and TNFα neutralizing antibodies or isotype control antibody before PAM3CSK4 injections. KSL SLAM cells in the bone marrow (e) and spleen (f) were determined by flow cytometry. In addition, whole spleen cells were plated on complete methylcellulose, and colonies counted after 7 days of growth at 37 °C (g); n=5–6 mice per group. For all panels, error bars represent mean±s.e.m., and P-values were determined by the two-tailed Student's t-test.