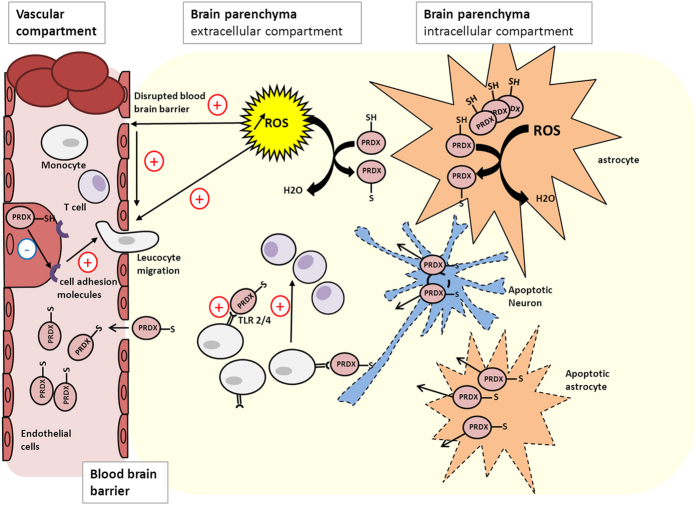
Figure 6. Different roles of peroxiredoxins during cerebral infarction.
During cerebral ischemia, peroxiredoxins reduce reactive oxygen species into less reactive components and inhibit expression of cell adhesion molecules in endothelial cells promoting leukocyte migration in the brain parenchyma. However, the oxidized form produced and released from apoptotic cells can activate monocytes and promote inflammation in the brain parenchyma. High serum levels of peroxiredoxins would result from production in endothelial cells and diffusion from the extracellular into the vascular compartment through disrupted blood brain barrier. PRDX: peroxiredoxin, TLR 2/4: toll like receptors 2 and 4, ROS: reactive oxygen species.