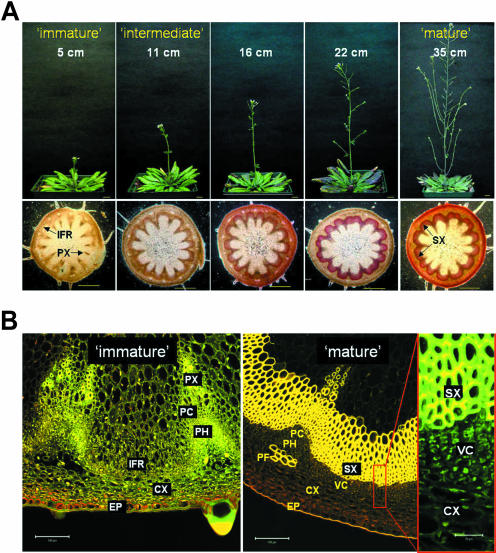
Figure 1.
Secondary xylem tissue development of Arabidopsis stem. A, Secondary xylem development is related to the plant stem height. All plants are the same age (8 weeks old) and have similar stem thickness, but differ in the height growth of inflorescence stems. The heights of the stems are indicated in upper panels. Basal level of the stem was cross-sectioned and stained with 2% phloroglucinol-HCl to visualize secondary xylem as red color in the lower section. Scale bars represent 1 cm in upper sections and 0.5 cm in lower sections. B, Secondary xylem developed from vascular cambium of the mature Arabidopsis stem. Detailed structure of immature and mature stem cross-section was obtained from confocal laser microscopy (see “Materials and Methods”). EP, epidermis; IFR, interfascicular region; PC, procambium; PH, phloem; PX, primary xylem; VC, vascular cambium; PF, phloem fiber; SX, secondary xylem. Bar indicates 0.2 mm of length.