Figure 5. Eomes acts independently of T-bet for GM-CSF regulation in CD4+ T cells.
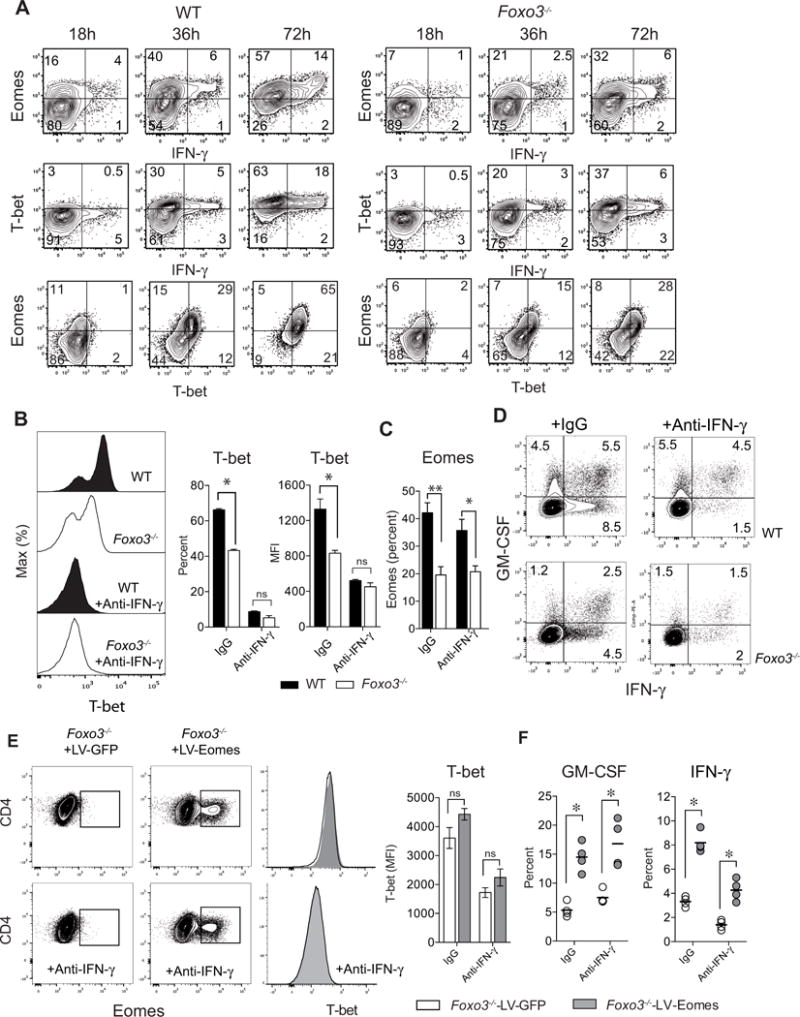
(A) Kinetics of T-bet, Eomes and IFN-γ expression in naive WT or Foxo3−/− CD4+ T cells stimulated with 2μg/ml of anti-CD3 mAbs for 18, 36 or 72 hours (n= 4 mice per genotype). (B) T-bet expression or (C) Eomes expression in naive WT (black bars/histograms) or Foxo3−/− (white bars/histograms) CD4+ T cells stimulated with anti-CD3 mAbs in the absence or presence of anti-IFN-γ blocking mAbs. (n= 4–5 mice per group). (D) Frequency of IFN-γ +, IFN-γ +-GM-CSF+ and GM-CSF+ producing cells in naive WT or Foxo3−/− CD4+ T cells cultured in the absence or presence of anti-IFN-γ neutralizing mAbs. (E) Eomes and T-bet expression in naive WT or Foxo3−/− CD4+ T cells transduced with either control (LV-GFP) or Eomes (LV-EOMES) expressing lentiviral particles in presence or absence of anti-IFN-γ mAbs. (F) Frequency of GM-CSF and IFN-γ producing cells in naive Foxo3−/− CD4+ T cells transduced either with control (LV-GFP, open bars/dots) or Eomes (LV-EOMES, grey bars/dots). Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Error bars, SEM.; P values (Mann–Whitney U test). See also Figure S5
