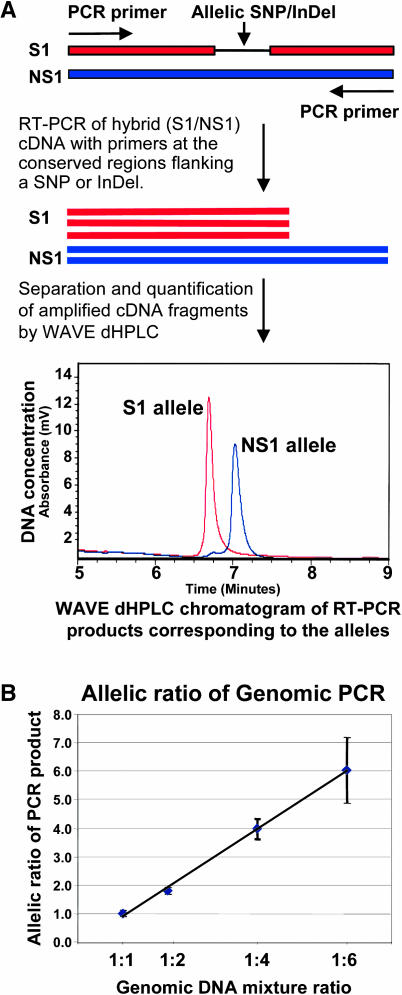
Figure 1.
Schematic Illustration of Allele Expression Analysis Using the WAVE dHPLC System and Genomic PCR as Control.
(A) RT-PCR and allele-specific cDNA quantification. The parental alleles of a gene are cloned and sequenced to find an allelic polymorphism, either SNPs or InDels, shown as the thin line. RT-PCR is then performed with hybrid cDNA using primers designed at the conserved region between the alleles. The RT-PCR products were separated and quantified by the WAVE dHPLC system. The longer DNA fragments corresponding to one parental allele have higher affinity than the shorter DNA fragments and, therefore, take a longer time to be eluted from the WAVE column. (In the case of SNPs, the allele-specific fragments were separated by differential melting temperature.) Chromatogram traces for each PCR were generated by UV detection. When both alleles are expressed, the two types of cDNA sequences could form two types of heteroduplex (on the left of the chromatogram in some hybrids if any) in addition to the two types of homoduplexes (corresponding to two alleles). The two types of heteroduplexes are eluted earlier than the homoduplexes because of the low affinity to the column and shown as one or two peaks depending on the separation condition. Peak areas corresponding to the homoduplexes and heteroduplexes were calculated by WAVEMAKER software. The x axis is the time in minutes when the DNA fragments are eluted out. The y axis is the UV absorbency unit measuring the DNA concentration or expression level. This analysis quantifies the allele-specific transcript in a relative ratio and does not measure the absolute transcript level expressed in the hybrid.
(B) Allelic ratio of PCR product from genomic DNA mixture series. The genomic PCR was used to test whether PCR amplification maintained the allelic ratio with different proportions of the allelic genomic DNA. Genomic DNA from parental inbreds S1 and NS1 were mixed according to the ratio of S1:NS1 as 1:1, 1:2, 1:4, and 1:6. We used gene-specific primers (LTP was used because of the available genomic DNA sequences and its dynamic allelic expression differences; see Results) for the PCR analysis. The amplified genomic DNA fragments, a mixture of the two parental alleles, were separated and quantified by the WAVE dHPLC system. Three replicates were done for each mixture, and the means of the genomic allelic ratio (NS1:S1) are shown with standard deviation (error bar). The allelic ratios of the genomic PCR product are not significantly different (P > 0.05) from the corresponding DNA mixture ratio.