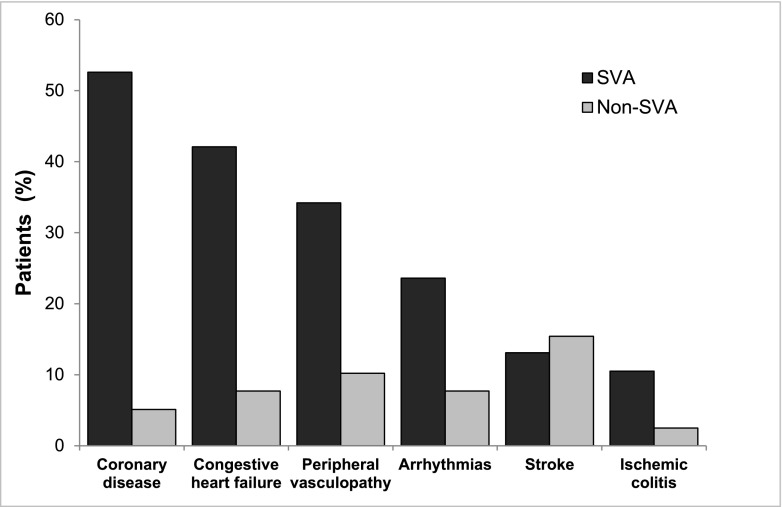
Figure 4.
Nonfatal cardiovascular events were more frequent in patients who developed supraventricular arrhythmias (SVAs). Coronary disease (52.6% versus 5.1%; P=0.001), congestive heart failure (42.1% versus 7.7%; P=0.001), peripheral vasculopathy (34.2% versus 10.2%; P=0.01), arrhythmias (23.6% versus 7.7%; P=0.04), stroke (13.1% versus 15.4%; P=0.78), and ischemic colitis (10.5% versus 2.5%; P=0.15).