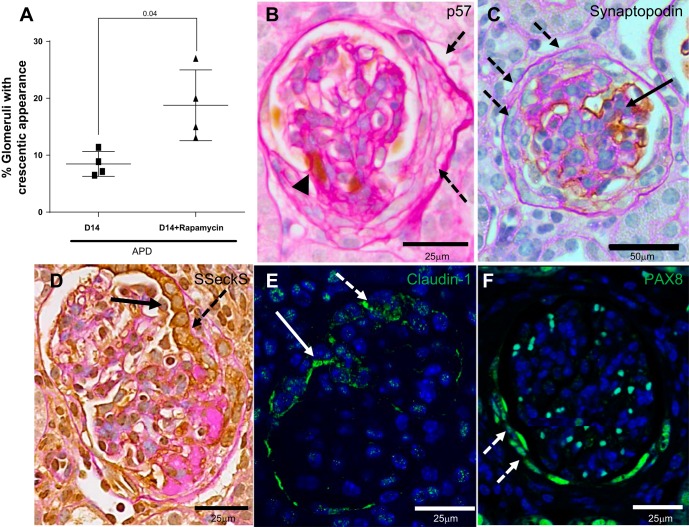
Fig. 5.
Glomerular crescents develop in a subset of glomeruli in APD mice given rapamycin. A: graph showing that the percentage of glomeruli exhibiting crescents, defined as two or more cell layers along Bowman's capsule, was higher in APD treated with rapamycin. B: representative high-power image (×400) of podocytes identified by p57 staining (brown nuclear stain, arrowhead) in sections counterstained with periodic acid Schiff stain from mice D14 APD given rapamycin. Dashed arrows indicates a crescent that is negative for p57. C: podocytes identified by synaptopodin staining (brown nuclear stain, solid arrow) in sections counterstained with periodic acid Schiff stain from mice D14 APD given rapamycin with crescent negative for synaptopodin staining (dashed arrow) but nonaffected area positive for synaptopodin (solid arrow). Representative image is at ×200 magnification. D: PECs identified by Src-suppressed C-kinase substrate (SSeCKS) staining (brown cytoplasmic stain on periodic acid Schiff background) in a glomerulus with a crescent indicated by dashed arrow at high power (×400). In the region of the crescent, PEC cells are cuboidal and stained positive for SSeCKS (solid arrow). E: crescent is positive for PEC marker claudin-1. Representative confocal microscopy image is of a glomeruli at high power (×400) stained for claudin-1 (green, cytoplasmic). Nuclei were stained blue with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Crescent is indicated by dashed white arrow. White solid arrow indicates claudin-1 staining on cytoplasmic border of PEC cell. F: representative confocal microscopy image of a glomerulus at high power (×400) stained for paired box gene 8 (PAX8; green) with DAPI nuclear stain. A crescent, indicated by dashed white arrow, is positive for PEC marker PAX8.