Fig. 1.
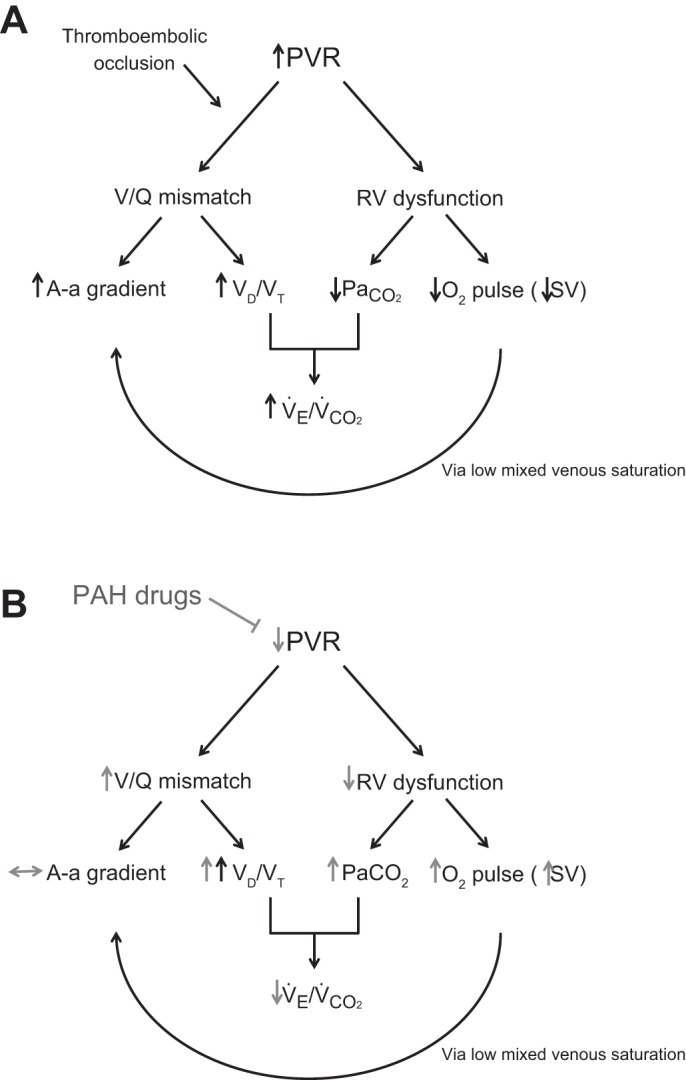
Pathophysiological mechanisms in chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension (CTEPH; A) and the effect of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH; B) therapy. A-a gradient, alveolar-arterial gradient; PaCO2, partial carbon dioxide arterial pressure; PVR, pulmonary vascular resistance; RV, right ventricular; V̇co2, carbon dioxide production; VD/VTphys, physiologic dead space; V̇e, ventilation; V/Q mismatch, ventilation/perfusion mismatch.
