Fig. 3.
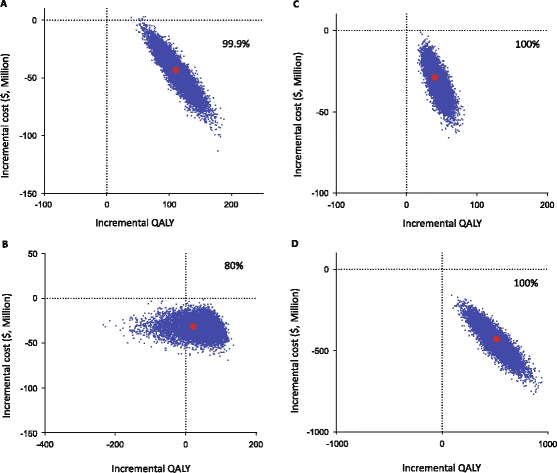
Probabilistic sensitivity analyses of patient-care strategies for a cohort of 100,000 patients. In this Monte Carlo simulation all parameters are simultaneously varied from their base-case values by sampling from probability distributions (Tables 1 and 2). The sampling process was repeated 10,000 times. The percent of the samplings that resulted in a test strategy with more QALYs at a lower cost compared with the comparable no-test strategy is shown in each panel. Each blue dot represents the result of one sampling of the parameters. The red dot represents the result using base-case parameters values. To clearly visualize the distributions of the simulation results, a randomly selected 1,000 (of the 10,000) samplings are plotted as blue dots in each panel. Panel a test-and-HST vs. MST; Panel b test-and-MST vs. Do-not-treat; Panel c test-and-MST vs. Do-not-treat, with the utility of being disease-free while taking a statin pill daily fixed at the base-case value. Panel d HST vs. MST
