Fig. 3.
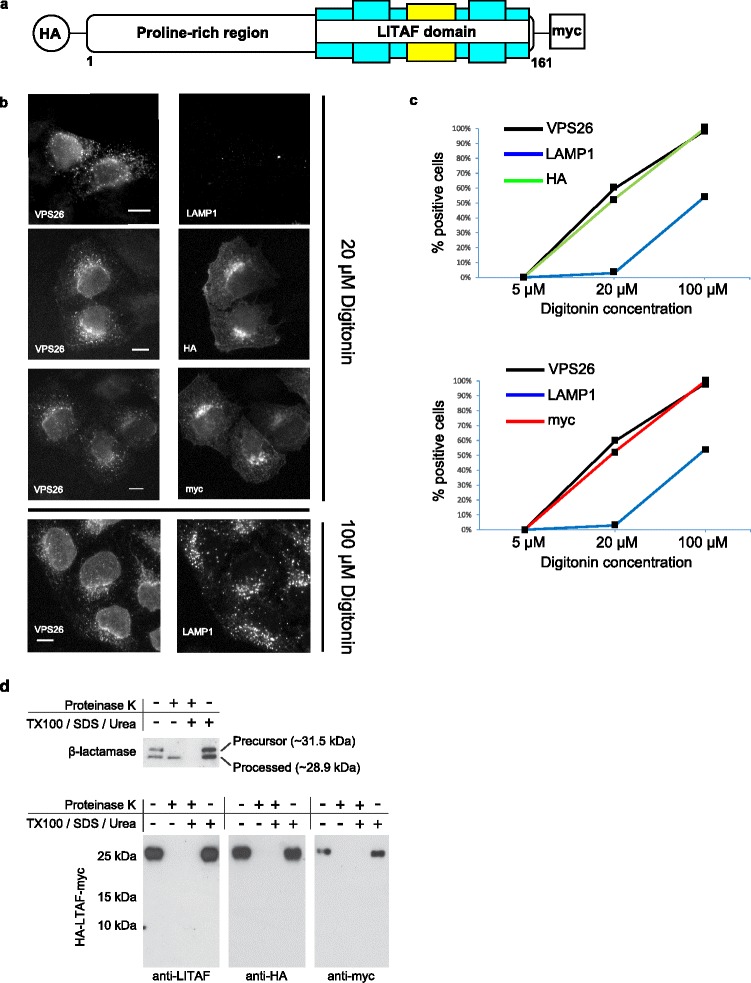
Membrane topology determination of LITAF. a Schematic diagram illustrating the LITAF protein tagged with HA at the N-terminus and myc at the C-terminus used in the experiments to determine the membrane topology. b Selective permeabilisation of the plasma membranes of HeLa cells stably expressing HA-LITAF-myc was achieved using 20 μM digitonin. Immunofluorescence microscopy was performed following incubation of the digitonin-permeabilised cells with antibodies towards HA and myc in addition to the control proteins, VPS26 and LAMP1, located on the cytosolic and luminal sides of endosomal membranes, respectively. The representative images show that both the N-terminal HA and C-terminal myc epitopes were detected concurrently with VPS26, indicating that both termini of LITAF are located on the cytosolic surface of membranes. In contrast, LAMP1 was not detected under these conditions. Permeabilsation of both plasma membrane and endosomal membranes was achieved at higher concentrations of digitonin as seen in the lower panel. c Representative graphs of a selective permeabilisation experiment illustrating the proportion of cells staining positive for HA (top panel) and myc (bottom panel) compared to VSP26 and LAMP1 (co-labelling and counting 400 cells) at increasing concentrations of digitonin. Note that all cells staining positive for HA were also positive for myc and that even at 100 μM digitonin, not all cells stained positive for LAMP1, indicating incomplete permeabilisation of endocytic vesicle membranes under these conditions. d HA-LITAF-myc was expressed using a rabbit reticulocyte lysate expression system in the presence of microsomal membranes to allow membrane insertion. A protease protection assay was then performed using proteinase K to determine the topology of the LITAF protein. In the presence of proteinase K, both N-terminal HA and C-terminal myc tags were digested, indicating that these epitopes are present on the surface of microsomal membranes (bottom panel). β-lactamase, containing a signal peptide that allows the translocation of a processed form to the interior of microsomal membranes, and hence protection from proteinase K digestion, was used as a control (top panel)
