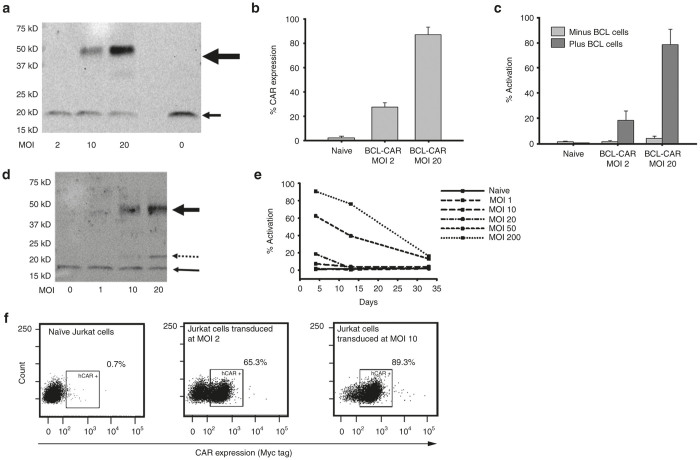
Figure 2.
VLR-CAR expression and activation of Jurkat cells when cocultured with cells expressing the target antigen. (a) Western blot using anti-CD3æ antibody showing BCL-VLR-CAR protein expression in whole cell lysates of Jurkat cells transduced at MOIs from 2 to 20. The bold arrow shows BCL-VLR-CAR and the thin arrow shows endogenously expressed CD3æ. (b) Flow analysis of myc expression on the surface of naive and transduced Jurkat cells at MOIs of 2 and 20. (c) Flow analysis of activation (CD69 expression) in naive Jurkat cells and Jurkat cells transduced with BCL-VLR-CAR in the absence or presence of BCL cells. Naive and transduced Jurkat cells not cocultured with BCL showed minimal activation. (d) Western blot using anti-CD3æ antibody showing increased CD5-VLR-CAR expression with increasing MOI. The bold arrow shows CD5-VLR-CAR, the thin arrow shows endogenously expressed CD3æ, and the dashed arrow shows a possible breakdown product of the CD5-VLR-CAR, which is not observed with the BCL-VLR-CAR. (e) Increased activation is observed in Jurkat cells transduced at increased MOIs with the CD5-VLR-CAR, but activation subsequently decreases over time in all transduction conditions. (f) VLR-CAR expression 35 days after transduction at MOIs of 0, 2, and 10. Values within the figures show the percentage of VLR-CAR positive cells. CAR, chimeric antigen receptor; MOI, multiplicity of infection; VLR, variable lymphocyte receptor.