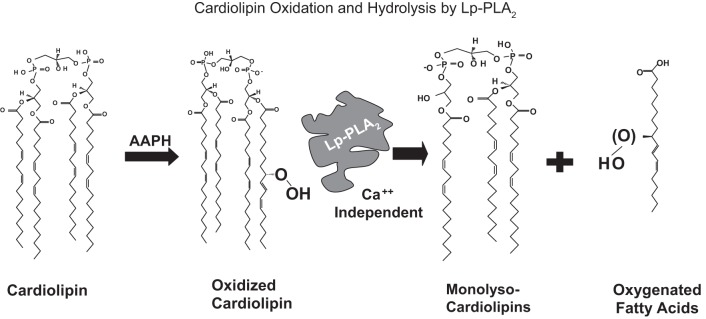
Fig. 2.
In vitro oxidation and hydrolysis of tetralinoleoyl CL. A cell-free in vitro system was developed with CL oxidation by the azo initiator, AAPH. Subsequently the CLox was hydrolyzed by the Ca++-independent Lp-PLA2, producing monolyso- and dilyso- (not shown) CL species, as well as oxygenated free fatty acids.