FIG 1 .
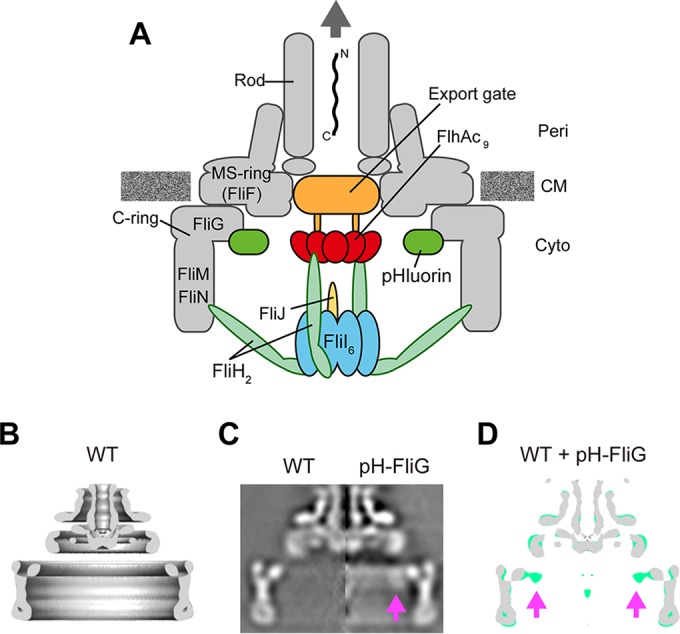
Location of the pHluorin(M153R) probe at the flagellar base. (A) Schematic diagram of the bacterial flagellar basal body with a type III export apparatus attached. The export apparatus consists of a PMF-driven transmembrane export gate made of FlhA, FlhB, FliO, FliP, FliQ, and FliR and a cytoplasmic ATPase complex consisting of FliH, FliI, and FliJ. To measure the local pH near the gate, the pHluorin(M153R) probe was fused to the N terminus of FliG. Peri, periplasm; CM, cytoplasmic membrane; Cyto, cytoplasm. (B) Averaged 3D image of the FBB purified from the Salmonella HK1002 strain (wild type [WT]). A c100 rotational symmetry was enforced for the refinement of the image processing. Side view of half-cut section is shown. (C) The axial sections of isolated FBB from HK1002 cells (wild type) (left) and TM041 cells [pHluorin(M153R)-fliG] cells (pH-FliG) (right). (D) Superposition of the wild-type FFB (gray) on the pHluorin(M153R)-FliG FBB (light green). The axial section images of the wild-type FBB and the pHluorin(M153R)-FliG FBB were processed and superimposed. The location of the pHluorin(M153R) probe is indicated by arrows. The pHluorin(M153R) position looked flexible due to the flexibility of the C-terminal region of pHluorin(M153R), thereby reducing the electron density of the pHluorin(M153R) probe.
