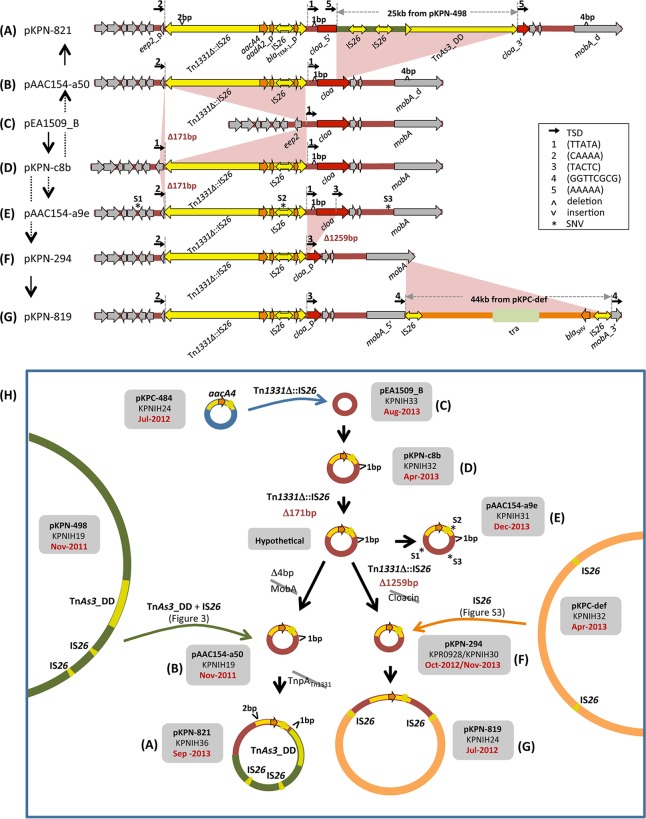
FIG 4 .
pAAC154 plasmid family within the NIH CC plasmid pool. (A to G) Schematics of the plasmid family members, showing their sequence relationships. Black vertical arrows mark the direction of evolution, where gray dashed lines indicate that there is an intermediate not detected within the plasmid pool. (A) Relative to the smallest family member, pEA1509_B (C), pKPN-821 has received a TnAs3_DD and IS26-mediated insertion of a ~25-kb fragment from pKPN-498 (Fig. 2) as well as an insertion of Tn1331Δ::IS26. There has also been a 2-bp DNA insertion within the tnpA gene of Tn1331Δ::IS26 that presumably disables the transposon. (B) pAAC154-a50 was recovered from the original NIH outbreak strain. There has been a 4-bp deletion within the mobA gene (also seen in pKPN-821 [A]) (27). (C) pEA1509_B is identical to a previously reported Enterobacter aerogenes plasmid (GenBank accession no. FO203353.1). (D) pKPN-c8b is related to pEA1509_B (C) by the insertion of Tn1331Δ::IS26. Tn1331Δ::IS26, a Tn3 family member, is a Tn1331 derivative (28) in which an internal insertion of IS26 partially deleted the aadA2 and blaTEM-1 genes, and removed the truncated tnpR of Tn1331 and the blaOXA-9 gene (8). Note that it has been previously referred to as ISSwi1-m2 (29). It carries an aacA4 [aac(6′)-Ib] gene encoding an aminoglycoside 6′-N-acetyltransferase that confers resistance to several aminoglycosides such as amikacin and kanamycin (30). This gene is retained intact through all the subsequent steps of the evolutionary pathway. (E) Deletion of 171 bp at the left end of Tn1331Δ::IS26 to form pAAC154-a9e is consistent with its intramolecular transposition. This reaction deleted one of the original flanking TTATA TSD sequences, labeled “1.” SNVs are numbered S1 to S3 and are marked by asterisks. (F) A second intramolecular transposition reaction by Tn1331Δ::IS26 appears to have removed the second TTATA copy and truncated the cloa gene in pKPN-294. (G) Relative to pKPN-294 (F), pKPN-819 appears to have received an IS26-mediated insertion of 44 kb from pKPC-def (see Fig. S3 in the supplemental material). One of the genes within the 44-kb fragment, blaSHV, codes for a beta lactamase; the fragment also bears a conjugal transfer operon, possibly important for continued plasmid fitness as the mobA gene was disrupted when IS26 transposed. (H) Summary of the transformation pathway of the plasmids from various patient strains. Note the temporal disconnect: pAAC154-a50 was isolated in November 2011 and pKPN-819 in July 2012. However, the ancestors of these plasmids were identified later.