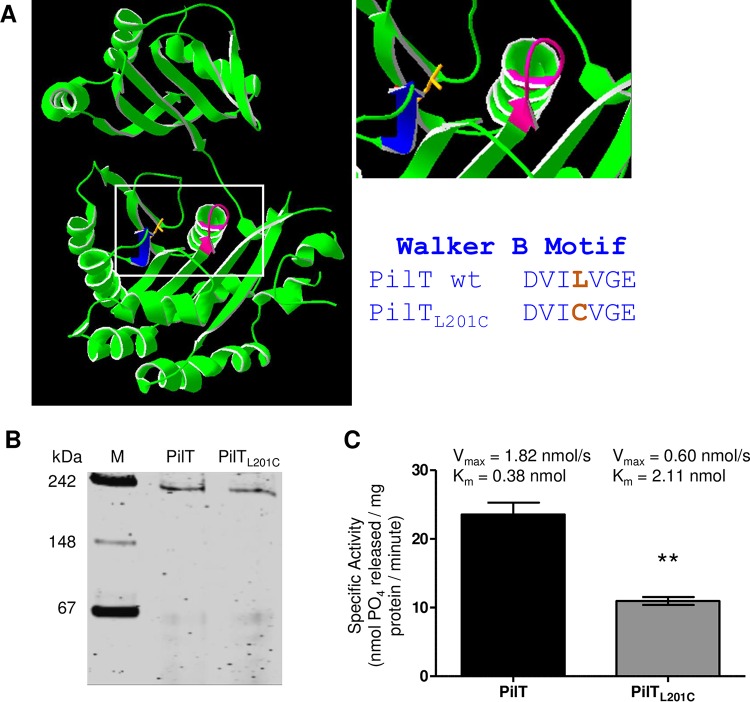
FIG 1 .
PilTL201C forms a hexamer but has reduced ability to bind and hydrolyze ATP. (A) Predicted structure of the N. gonorrhoeae PilT monomer (left), close-up view of its ATP binding site (top right), and residues of the Walker B domain of wt PilT and PilTL201C (bottom right). Walker A domain (magenta); Walker B domain (blue); L201 side chain (orange). (B) Migration of purified PilT and PilTL201C in a nondenaturing 6.5% acrylamide gel stained with Coomassie blue. Predicted molecular mass of the PilT hexamer is 222 kDa. (C) ATPase activity, Vmax, and Km values of PilT and PilTL201C hexamers. Values are the average results from 3 independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. **, P < 0.01, Student’s two-tailed unpaired t test.