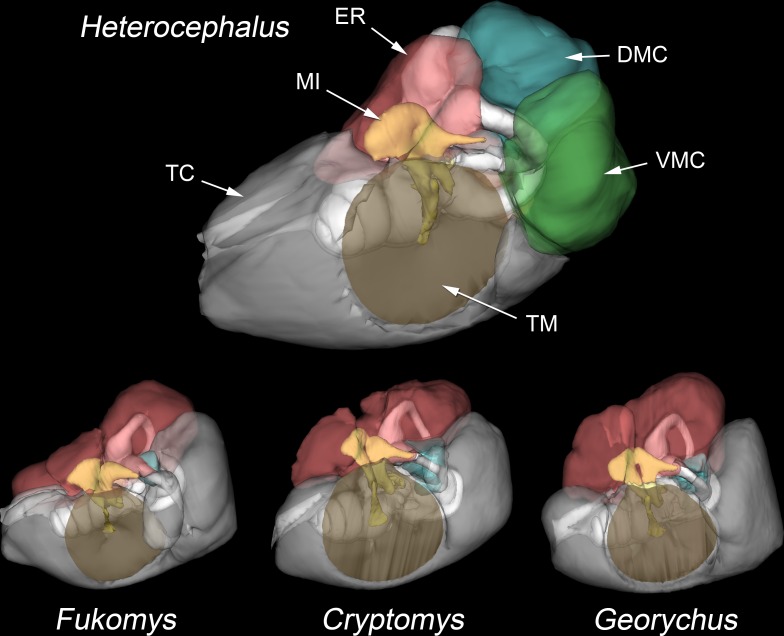
Fig 5. Middle ear cavities of bathyergids.
WinSurf reconstructions of the left middle ear cavities and associated structures in four species of bathyergids (Heterocephalus glaber, Fukomys micklemi, Cryptomys hottentotus and Georychus capensis), from lateral and slightly anterior views. The walls of the middle ear cavities are shown semitranslucent. Positions of the tympanic membranes are indicated by brown shading. The epitympanic recess is colour-coded red, the dorsal mastoid cavity blue and the ventral mastoid cavity green. The ossicles are yellow. The posteromedial mastoid cavity, present only in Heterocephalus, is not visible in this view. The posterior parts of the middle ear cavities of the other species extend into the mastoid region and are equivalent to the ventral mastoid cavity of Heterocephalus, but they lack constricted entrances and so have not been separately coloured. Not to scale. APSC = ampulla for posterior semicircular canal; ASC = anterior semicircular canal; C = cochlea; DMC = dorsal mastoid cavity; ED = bony tube for endolymphatic duct; ER = epitympanic recess; FP = footplate of stapes; HM = head of malleus; LA = lenticular apophysis of incus; LPI = long process of incus; LSC = lateral semicircular canal; MI = malleoincus; MM = manubrium of malleus; OW = oval window; PC = posterior crus of stapes; PD = bony tube for perilymphatic duct (canaliculus cochleae); PMC = posteromedial mastoid cavity; PSC = posterior semicircular canal; RW = round window; SPI = short process of incus; TC = tympanic cavity; TM = tympanic membrane; TT = tensor tympani tendon; V = vestibule of inner ear; VMC = ventral mastoid cavity.