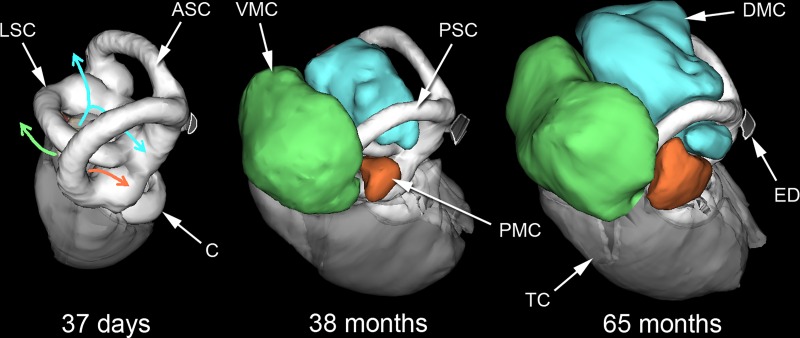
Fig 6. Bony labyrinths and mastoid cavities of Heterocephalus.
WinSurf reconstructions of the left bony labyrinths and mastoid cavities of three Heterocephalus specimens of different ages, seen from approximately posterior views. In the youngest specimen on the left, coloured arrows indicate the future directions of expansion of the middle ear cavity into the mastoid region. Blue = dorsal mastoid cavity; green = ventral mastoid cavity; orange = posteromedial mastoid cavity. The 38-month-old specimen had smaller mastoid cavities than many younger specimens, so this diagram should not be taken to indicate a strict temporal sequence. APSC = ampulla for posterior semicircular canal; ASC = anterior semicircular canal; C = cochlea; DMC = dorsal mastoid cavity; ED = bony tube for endolymphatic duct; ER = epitympanic recess; FP = footplate of stapes; HM = head of malleus; LA = lenticular apophysis of incus; LPI = long process of incus; LSC = lateral semicircular canal; MI = malleoincus; MM = manubrium of malleus; OW = oval window; PC = posterior crus of stapes; PD = bony tube for perilymphatic duct (canaliculus cochleae); PMC = posteromedial mastoid cavity; PSC = posterior semicircular canal; RW = round window; SPI = short process of incus; TC = tympanic cavity; TM = tympanic membrane; TT = tensor tympani tendon; V = vestibule of inner ear; VMC = ventral mastoid cavity.