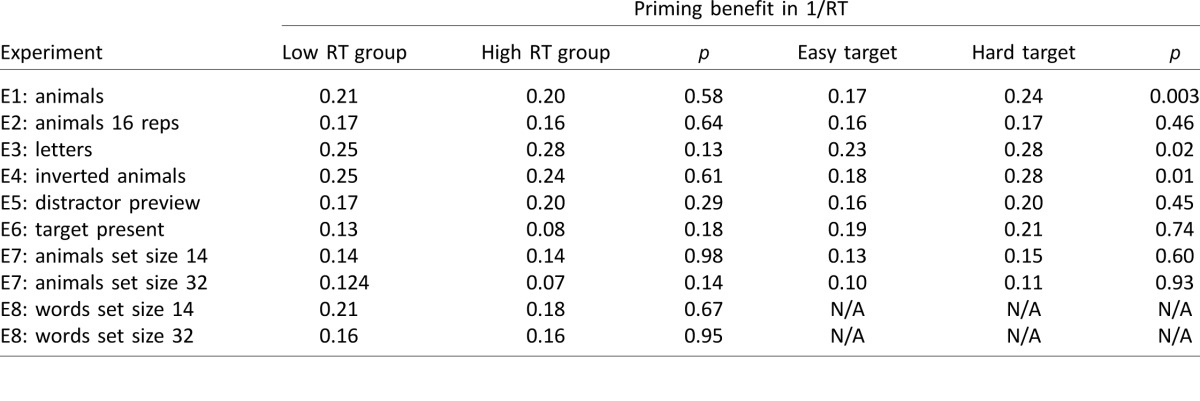
Table 4.
Priming benefit as a function of search difficulty and search asymmetry. Notes: Here we have compared the priming benefit (difference in 1/RT between target preview and unrelated preview) by separating all significant searches into two equal groups (low RT and high RT). The column denoted by p represents the statistical significance of a paired comparison (paired t test) performed between the easy and hard searches. Likewise, to investigate whether the priming benefit is influenced by search asymmetry, we divided the searches for each significantly primed image pair (A, B) into those corresponding to the easy target or the hard target in the unrelated priming condition. The priming benefit for the easy and hard targets is shown with column p denoting the statistical significance of the comparison (paired t test). Entries corresponding to easy and hard targets in the words experiment are marked N/A because search asymmetries are no longer meaningful for heterogeneous searches with one target and two distractors.