Fig. 1. ARHGAP11A and ARHGAP11B genomic, pre-mRNA, mRNA, and protein structures.
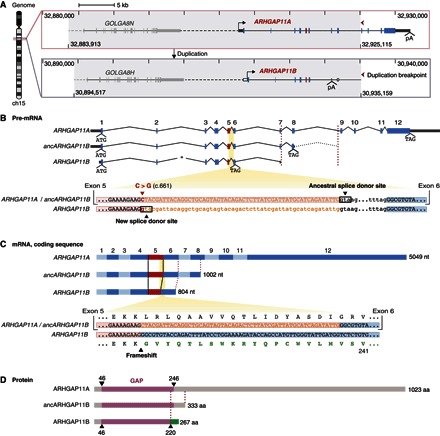
(A) Gene structure and genomic context of human ARHGAP11A (top) and ARHGAP11B (bottom). Gray areas indicate the duplicated genomic region (40.642 Mb), which comprises the GOLGA8 and ARHGAP11 genes. Tick marks and numbers indicate genomic coordinates on chromosome 15 (GRCh37/hg19). Red arrowheads point to the 3′ duplication break point, highlighting the partial nature of the ARHGAP11 duplication. Continuous and dashed horizontal lines indicate intragenic and intergenic regions, respectively. Transcription start sites (forward arrows) and polyadenylation sites (pA) are shown. Rectangles indicate exons; dark gray, untranslated regions; blue and red, protein-coding sequences (red, exon 5); white, exonic sequences of ARHGAP11A that are duplicated but typically untranscribed in modern ARHGAP11B. The duplicated GOLGA8 gene 5′ to ARHGAP11 is depicted in light gray. Image was adapted from the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) Genome Browser. (B) ARHGAP11A, predicted ancestral ARHGAP11B (ancARHGAP11B), and modern ARHGAP11B pre-mRNAs (top). Translation start (ATG) and stop (TAG) codons are indicated. Numbers (1 to 12) indicate ARHGAP11A exons, 1 to 8 of which were duplicated. Left red dashed line indicates the position of the pA site in exon 7 of modern ARHGAP11B relative to exon 7 of ARHGAP11A and ancARHGAP11B. Dotted intron line 3′ to the predicted ancARHGAP11B stop codon indicates the duplicated portion of ARHGAP11A intron 8 until the duplication break point (right red dashed line). Asterisk indicates a 593-bp deletion in modern ARHGAP11B intron 2. (B) Alignment of ARHGAP11A/B homologous sequences (bottom) encompassing the 3′ end of exon 5 (red background) and 5′ end of exon 6 (blue background), interspaced by intron 5. Exonic and intronic nucleotide (nt) sequences are displayed in uppercase and lowercase letters, respectively. The C→G base substitution (red, position c.661) produces a new splice donor site in modern ARHGAP11B, 55-nt 5′ to the ancestral one. As a consequence, these 55 nt (orange sequences) become intronic. (C) ARHGAP11A, ancARHGAP11B, and modern ARHGAP11B coding sequences (top). Alternating light-dark blue rectangles indicate exons. Black lines highlight the shortening of modern ARHGAP11B exon 5. (C) Alignment of ARHGAP11A/B coding sequences (bottom) encompassing the 3′ end of exon 5 and the 5′ end of exon 6, with the corresponding amino acid sequences (until residue 241) depicted above and below. The 55-nt sequence corresponding to the 3′ end of ARHGAP11A exon 5 (orange) is spliced out from the modern ARHGAP11B mRNA. The resulting frameshift generates a novel C-terminal amino acid sequence (green) unique to modern ARHGAP11B. (B and C) Note that all RNA sequences are depicted with T instead of U. (D) ARHGAP11A, ancARHGAP11B, and modern ARHGAP11B protein structures showing the conserved portions of the ARHGAP11A GAP domain (purple) and the novel C-terminal domain of modern ARHGAP11B (green) starting at residue 221. aa, amino acids.
