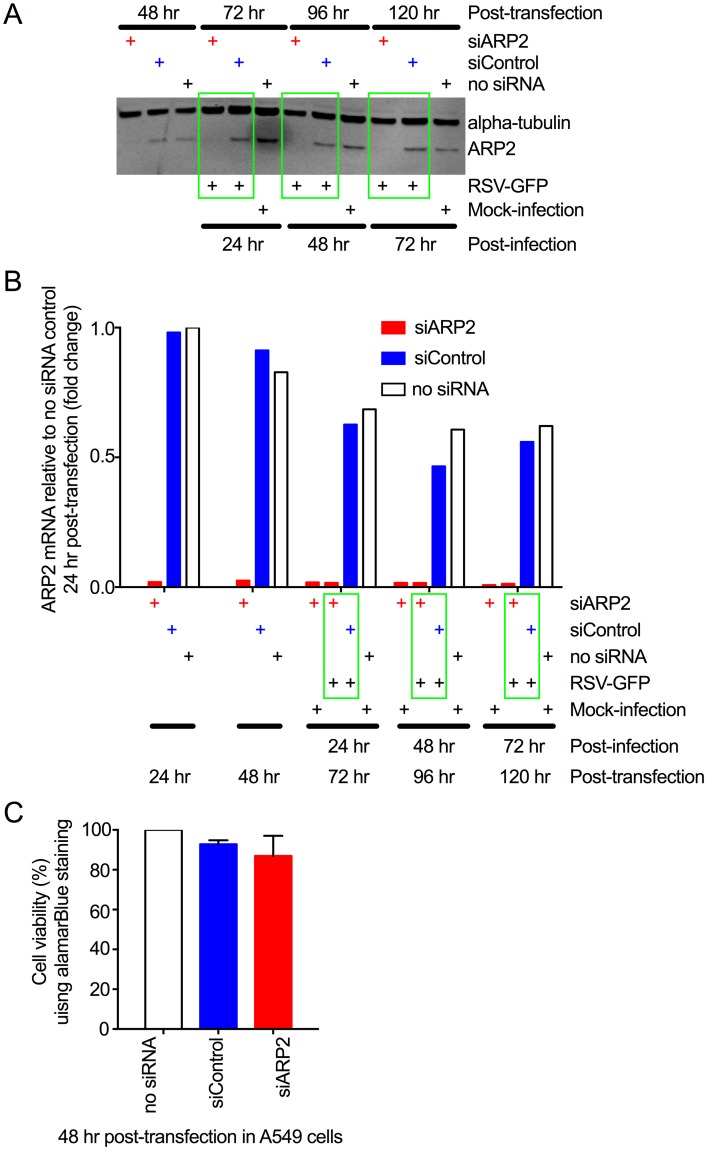
Fig 1. ARP2 knockdown in human respiratory epithelial A549 cells.
(A) Knockdown of ARP2 protein expression. Replicate monolayers of A549 cells were transfected with siARP2, siControl, or no siRNA, as indicated. At 48 hr post-transfection, one set of monolayers was harvested. The others were infected with RSV-GFP (MOI = 1) or mock-infected, and harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi, as indicated. The cells were processed for Western blotting. ARP2 protein was detected using a primary rabbit mAb and an anti-rabbit IgG IRDye800 secondary Ab. Alpha-tubulin, as a loading control, was detected with a primary mouse mAb and an anti-mouse IgG IRDye680 secondary Ab. Bound antibodies were visualized by infrared fluorescence. One representative of four independent experiments is shown. (B) Knockdown of ARP2 mRNA expression. A549 cells were transfected with siARP2, siControl, or no siRNA, as indicated. Sets of monolayers were harvested 24 and 48 hr post-transfection. The remaining monolayers were infected with RSV-GFP (MOI = 1) or mock-infected, and harvested at 24, 48, and 72 hpi, as indicated. Total cell-associated ARP2 mRNA was quantified by real-time PCR using a TaqMan assay for ARP2. 18S ribosomal RNA was used as an endogenous control for normalization of each reaction, and the values of ARP2 expression are shown as fold-change relative to the no-siRNA control 24 hr post-transfection. Each sample was tested in quadruplicate by TaqMan assay and the averages are presented. (C) ARP2 knockdown did not reduce cell viability. A549 cells were transfected with siARP2, siControl or no siRNA for 48 hr. Cell viability was compared using alamarBlue and expressed relative to the no-siRNA control. Data from three independent experiments, each done in triplicate were combined for analysis. Error bars show standard deviation (SD).