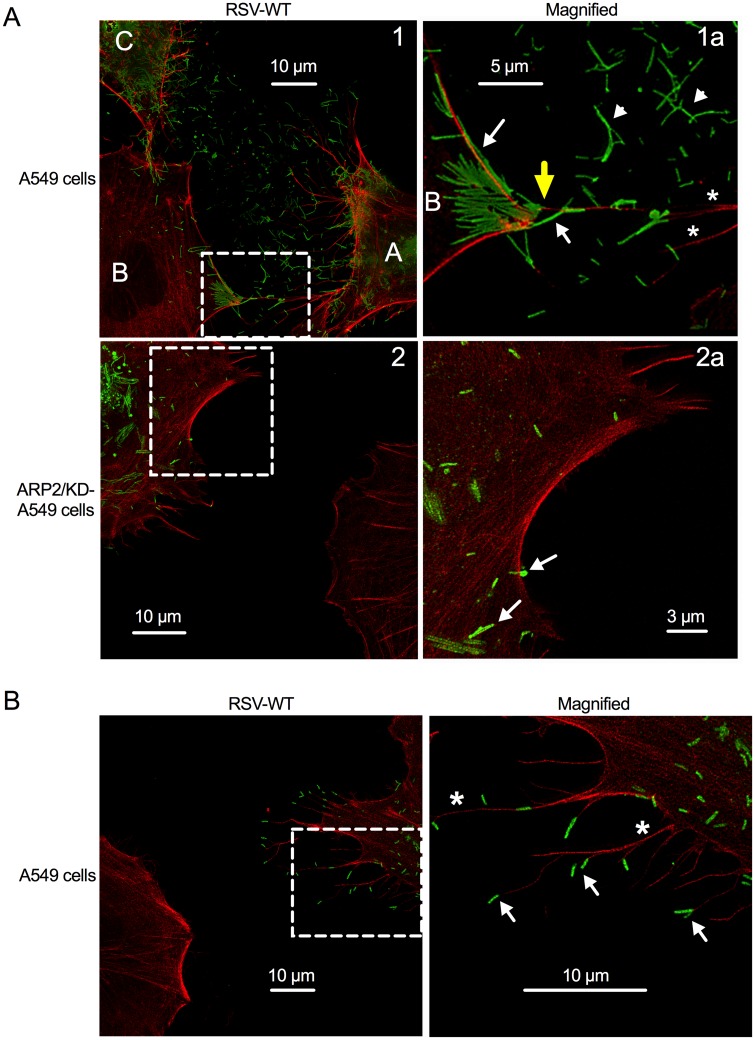
Fig 8. RSV appears to use filopodia for cell-to-cell spread.
(A, B) Stimulated emission depletion (STED) imaging of filopodia and virus filaments on RSV-infected cells. A549 cells or ARP2/KD-A549 cells (i.e., stable ARP2 knockdown) were infected with RSV-WT (MOI = 1). At 24 hpi, cells were fixed and permeabilized. F-actin was visualized by rhodamine phalloidin (red); immunostaining for RSV F was done with an RSV F mAb, followed by secondary antibody conjugated with AlexaFluor647 (pseudocolored in green; part A, top panel) or AlexaFluor488 (green; part A, bottom panel, and part B). Examples of filopodia are indicated with asterisks, and examples of what appear to be released filamentous RSV particles are indicated with arrowheads, and examples of cell-associated and filopodia-associated RSV are indicated with arrows. The areas in Panels 1 and 2 (left) that are outlined with dashed boxes are enlarged in panels 1a and 2a, respectively (right). Part (A) illustrates that the filopodia of the RSV-infected cells (panel 1, labeled A and C) appear to convey RSV particles to a neighboring cell (labeled B); in the enlargement 1a, a filopodium-cell junction is indicated with a yellow arrow. In panel 2 and enlargement 2a, filopodia-driven cell-to-cell spread was not evident. Part (B) illustrates the RSV virions at the tip of filopodia.