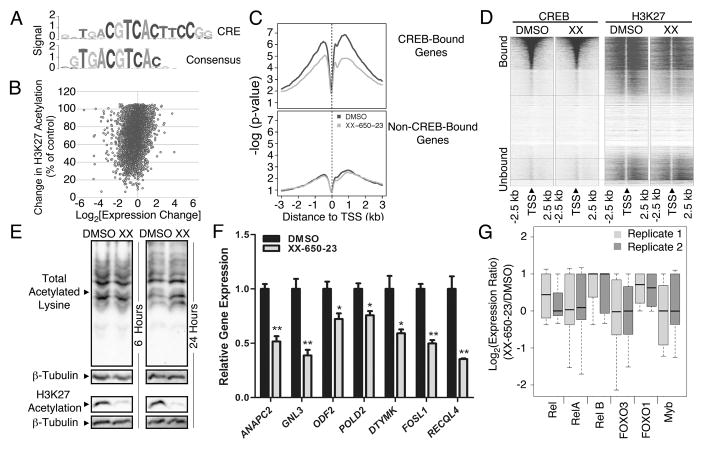
Fig. 3. Specificity of CREB Inhibition.
A) The consensus sequence obtained following CREB ChIP-Seq, mapped against the canonical CRE element sequence. B) Relationship between H3K27 acetylation and CREB-driven gene expression. RNA-Seq, CREB ChIP-Seq and H3K27 histone acetylation-Seq were performed on KG-1 cells treated with 5 μM XX-650-23 or 0.1% DMSO. Combined analysis defined the set of genes bound by CREB in AML cells, and alterations in transcription and histone acetylation occurring secondary to XX-650-23 at those loci. The percent of histone acetylation remaining following treatment with XX-650-23 is plotted versus the corresponding change in gene expression for all CREB-bound genes identified by CREB ChIP-Seq. C) Changes in H3K27 acetylation for CREB-bound and -unbound genes were averaged and plotted against base-pair distance to transcriptional start sites (TSS) following XX-650-23 or DMSO treatment. Non-CREB-bound genes show no significant change in H3K27 acetylation following XX-650-23 treatment. D) Heatmap of CREB binding and H3K27 acetylation relative to TSS in DMSO and XX-650-23-treated samples. H3K27 signal intensity, but not CREB binding signal intensity, decreased following XX-650-23. E) Western blot of total and H3K27-specific histone acetylation following XX-650-23 treatment following 6 or 24 hours of DMSO or XX-650-23 treatment. Representative blots of at least three independent experiments are shown. F) RT-PCR confirmed downregulation of CREB-bound genes identified on RNA-Seq following 12 hours of XX-650-23 treatment of KG-1 cells for all genes shown. Data are graphed as mean ± SEM (n = 3), *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001, t-test. G) RNA-Seq analysis demonstrated that the activity of six CBP-bound transcription factors remains unchanged following XX-650-23 treatment.