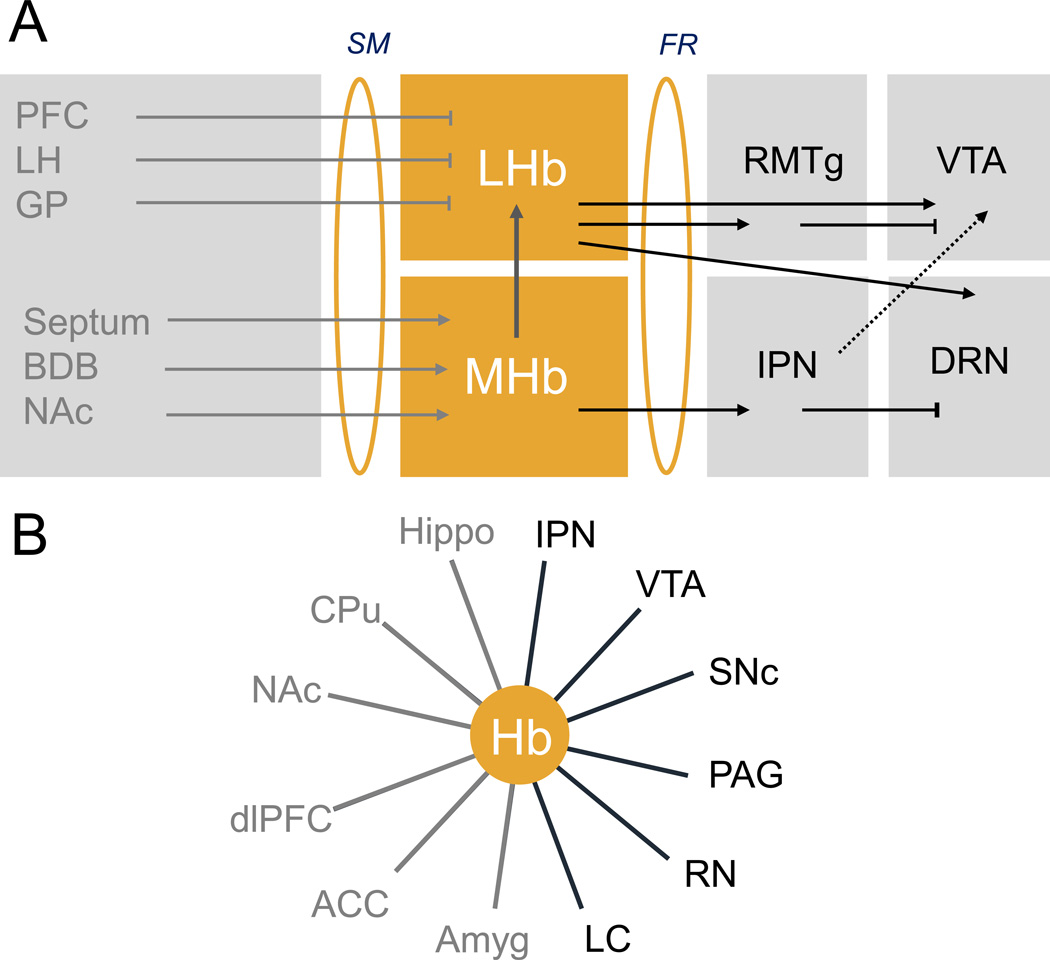
Figure 1. Habenula connectivity in rodents and humans.
Key pathways connecting medial habenula (MHb) and lateral habenula (LHb), the two subdivisions of the Hb, to other brain structures. Habenula connectivity is embedded in brain circuits classically described as reward and emotion circuits, whose dysfunction is associated to psychiatric diseases reviewed here. A. Structural connectivity in animal studies: The lateral Hb (LHb) receives inhibitory inputs from the prefrontal cortex (PFC), ventral pallidum, globus pallidus (GP) and lateral hypothalamus (LH) through the stria medullaris (SM) and, in turn, sends information to monoaminergic nuclei (5). Projections of LHb to dopaminergic neurons have been best described, and include direct (ventral tegmental area (VTA), see (100)) and indirect (tail VTA, see (101, 102)) projections. A recent tracing study further revealed an equal number of LHb projections to either dopaminergic (VTA) or serotonergic (dorsal raphe (DR) and median raphe nucleus (MnR)) nuclei, which are mostly but not exclusively segregated, indicating that LHb regulates the two monoamine nuclei either independently (the vast majority of LHb projecting neurons) or jointly (few heterogeneously distributed LHb projecting neurons) (103); both projections are excitatory (11, 104). The medial Hb (MHb) circuitry is less well known. The medial nucleus receives mainly excitatory inputs from the septum, nucleus accumbens (NAc) and broca diagonal band (BDB) (4, 5). and has excitatory projections to the rostromedial tegmental nucleus (RMTg) but mainly and massively to the interpeduncular nucleus (IPN), which in turn projects to the VTA and possibly the raphe nuclei (104). Thus, both MHb and LHb regulate in turn the VTA, DRN and possibly other midbrain and hindbrain structures such as the Locus Coereulus (LC) (103). Asymmetrical projections from MHb to LHb have been described (17). B- Functional connectivity in human studies: Hb connectivity established for both forebrain (in grey) and midbrain/hindbrain (in black) structures by fMRI (10, 21, 105). Abbreviations: CPu: caudate Putamen; Hippo: Hippocampus; Amyg: Amygdala; SNC: substantia nigra compacta; PAG: periaqueductal gray; RN: Raphe Nucleus; LC: locus coeruleus; ACC: anterior cingulate cortex.