Figure 1.
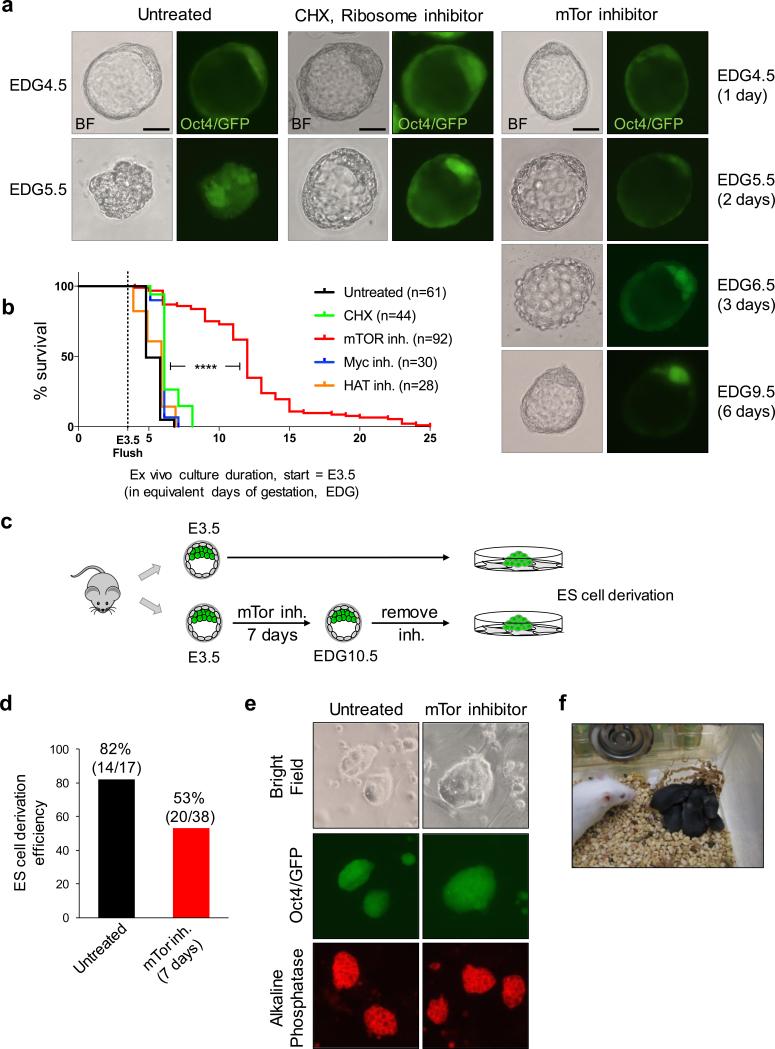
mTor inhibition induces blastocyst pausing ex vivo. a, Representative images of bright field and Oct4/GFP expression of blastocysts cultured ex vivo under indicated conditions. Scale bars = 25 μm. b, Kaplan-Maier survival curves of blastocysts cultured ex vivo with inhibitors. n, number of blastocysts tested. ****=P-value<0.0001 from log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test. c, Workflow of ES cell derivation from untreated or mTor-inhibited embryos. d, ES cell derivation efficiency from untreated and mTor-inhibited embryos. The reduced efficiency of derivation from mTor-inhibited embryos may be due to a lower frequency of hatching from the zona pellucida. e, Representative images of bright field, Oct4/GFP (passage 2) and alkaline phosphatase staining (passage 4) of ES cells derived from untreated and mTor-inhibited embryos. f, Live-born mice generated by transfer of mTor-inhibited blastocysts at EDG8.5 into surrogate females. See Extended Data Fig. 2a for details.