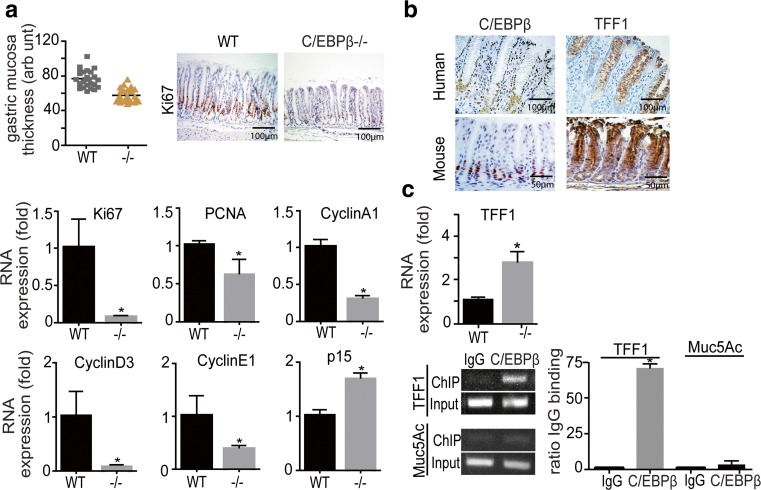
Fig. 2.
Analysis of the gastric phenotype of the C/EBPβ knockout (KO) mouse. a Quantification of the C/EBPβ KO mice and WT antral gastric mucosa thickness (in arbitrary units). Adjacent immunohistochemical panel depicts the reduction of Ki67-positive cells in the C/EBPβ KO mucosa. Lower panels show qPCR evaluation of Ki67, PCNA, Cyclin A1, D3, E1, and p15 in the gastric mucosa of WT and C/EBPβ KO mouse stomach (five animals/group, 3 months old). Expression values were first normalized to GAPDH expression and values are presented as fold of WT expression. b Mutually exclusive expression of TFF1 and C/EBPβ in the normal human (upper panel) and mouse (lower panel) stomach epithelium; C/EBPβ is expressed in proliferative cells of the neck zone and TFF1 in differentiated mucous epithelium. c Increased expression of mRNA of differentiation protein TFF1, in the C/EBPβ KO mouse mucosa as measured by qPCR. Lower panel show ChIP assay on disaggregated wt mouse stomach cells, showing in vivo binding of C/EBPβ to the TFF1 promoter both on an agarose gel (left) and by qPCR quantification. Results are presented as ratio to anti-IgG control binding. Binding to the Muc5ac promoter was used as a negative control. All bar graphs represent the result of at least three independent measurements; asterisk indicates p < 0.005